The budding yeast PP2ACdc55 protein phosphatase prevents the onset of anaphase in response to morphogenetic defects
- PMID: 17502422
- PMCID: PMC2064206
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200609088
The budding yeast PP2ACdc55 protein phosphatase prevents the onset of anaphase in response to morphogenetic defects
Abstract
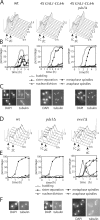
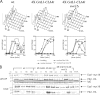
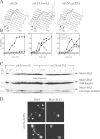
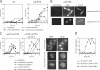
Faithful chromosome transmission requires establishment of sister chromatid cohesion during S phase, followed by its removal at anaphase onset. Sister chromatids are tethered together by cohesin, which is displaced from chromosomes through cleavage of its Mcd1 subunit by the separase protease. Separase is in turn inhibited, up to this moment, by securin. Budding yeast cells respond to morphogenetic defects by a transient arrest in G2 with high securin levels and unseparated chromatids. We show that neither securin elimination nor forced cohesin cleavage is sufficient for anaphase in these conditions, suggesting that other factors contribute to cohesion maintainance in G2. We find that the protein phosphatase PP2A bound to its regulatory subunit Cdc55 plays a key role in this process, uncovering a new function for PP2A(Cdc55) in controlling a noncanonical pathway of chromatid cohesion removal.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwal, R., and O. Cohen-Fix. 2002. Mitotic regulation: the fine tuning of separase activity. Cell Cycle. 1:255–257. - PubMed
-
- Alexandru, G., F. Uhlmann, K. Mechtler, M. Poupart, and K. Nasmyth. 2001. Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell. 105:459–472. - PubMed
-
- Bachant, J., A. Alcasabas, Y. Blat, N. Kleckner, and S.J. Elledge. 2002. The SUMO-1 isopeptidase Smt4 is linked to centromeric cohesion through SUMO-1 modification of DNA topoisomerase II. Mol. Cell. 9:1169–1182. - PubMed
-
- Charles, J.F., S.L. Jaspersen, R.L. Tinker-Kulberg, L. Hwang, A. Szidon, and D.O. Morgan. 1998. The Polo-related kinase Cdc5 activates and is destroyed by the mitotic cyclin destruction machinery in S. cerevisiae. Curr. Biol. 8:497–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

