Cell adhesion induces p27Kip1-associated cell-cycle arrest through down-regulation of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase pathway in mantle-cell and other non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 17502456
- PMCID: PMC1975846
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-060350
Cell adhesion induces p27Kip1-associated cell-cycle arrest through down-regulation of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase pathway in mantle-cell and other non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas
Abstract
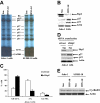
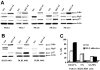
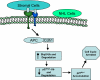
Mounting evidence suggests that dynamic interactions between a tumor and its microenvironment play a critical role in tumor development, cell-cycle progression, and response to therapy. In this study, we used mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) as a model to characterize the mechanisms by which stroma regulate cell-cycle progression. We demonstrated that adhesion of MCL and other non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cells to bone marrow stromal cells resulted in a reversible G(1) arrest associated with elevated p27(Kip1) and p21 (WAF1) proteins. The adhesion-mediated p27(Kip1) and p21 increases were posttranslationally regulated via the down-regulation of Skp2, a subunit of SCF(Skp2) ubiquitin ligase. Overexpression of Skp2 in MCL decreased p27(Kip1), whereas inhibition of Skp2 by siRNA increased p27(Kip1) and p21 levels. Furthermore, we found cell adhesion up-regulated Cdh1 (an activating subunit of anaphase-promoting complex [APC] ubiquitin ligase), and reduction of Cdh1 by siRNA induced Skp2 accumulation and hence p27(Kip1) degradation, thus implicating Cdh1 as an upstream effector of the Skp2/p27(Kip1) signaling pathway. Overall, this report, for the first time, demonstrates that cell-cell contact controls the tumor cell cycle via ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathways in MCL and other NHLs. The understanding of this novel molecular pathway may prove valuable in designing new therapeutic approaches for modifying tumor cell growth and response to therapy.
Figures


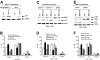

Similar articles
-
TGF-β activates APC through Cdh1 binding for Cks1 and Skp2 proteasomal destruction stabilizing p27kip1 for normal endometrial growth.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(7):931-47. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1150393. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26963853 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and progesterone regulate p27kip1 levels via the ubiquitin-proteasome system: pathogenic and therapeutic implications for endometrial cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046072. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029392 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma protein and anaphase-promoting complex physically interact and functionally cooperate during cell-cycle exit.Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Feb;9(2):225-32. doi: 10.1038/ncb1532. Epub 2006 Dec 24. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17187060
-
Don't skip the G1 phase: how APC/CCdh1 keeps SCFSKP2 in check.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):850-2. Epub 2004 Jul 14. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15190201 Review.
-
p27(Kip1) signaling: Transcriptional and post-translational regulation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Nov;68:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.08.005. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26279144 Review.
Cited by
-
Adhesion to fibronectin induces p27(Kip1) nuclear accumulation through down-regulation of Jab1 and contributes to cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) in RPMI 8,226 cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Jan;386(1-2):177-87. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1856-7. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24170542
-
Autophagy and Hepatic Tumor Microenvironment Associated Dormancy.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021 Dec;52(4):1277-1293. doi: 10.1007/s12029-021-00774-z. Epub 2021 Dec 18. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34921672 Review.
-
A novel 3D culture model recapitulates primary FL B-cell features and promotes their survival.Blood Adv. 2021 Dec 14;5(23):5372-5386. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003949. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 34555842 Free PMC article.
-
Parkin New Cargos: a New ROS Independent Role for Parkin in Regulating Cell Division.React Oxyg Species (Apex). 2016;2(5):315-324. doi: 10.20455/ros.2016.857. React Oxyg Species (Apex). 2016. PMID: 28920079 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor microenvironment is a dominant force in multidrug resistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2012 Feb-Apr;15(1-2):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Drug Resist Updat. 2012. PMID: 22335920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Campo E, Raffeld M, Jaffe ES. Mantle-cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 1999;36:115–127. - PubMed
-
- Viswanatha D, Foucar K. Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma involving bone marrow. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2003;20:196–210. - PubMed
-
- Gibson LF. Survival of B lineage leukemic cells: signals from the bone marrow microenvironment. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:19–27. - PubMed
-
- Damiano JS, Dalton WS. Integrin-mediated drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;38:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Hazlehurst LA, Damiano JS, Buyuksal I, Pledger WJ, Dalton WS. Adhesion to fibronectin via beta1 integrins regulates p27Kip1 levels and contributes to cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR). Oncogene. 2000;19:4319–4327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

