Exposing the core promoter is sufficient to activate transcription and alter coactivator requirement at RNR3
- PMID: 17502614
- PMCID: PMC1885588
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0701666104
Exposing the core promoter is sufficient to activate transcription and alter coactivator requirement at RNR3
Abstract
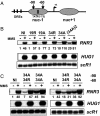
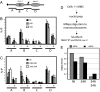
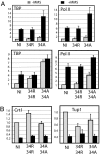
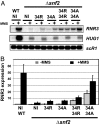
Chromatin is a formidable barrier to transcription. Nucleosome density is lowest over the regulatory regions of active genes, and many repressed genes have a tightly positioned nucleosome over their core promoter. However, it has not been shown that nucleosome positioning is sufficient for repression or whether disrupting a core promoter nucleosome specifically can activate gene expression in the absence of activating signals. Here we show that disrupting the nucleosome over the core promoter of RNR3 is sufficient to drive preinitiation complex assembly and activate transcription in the absence of activating signals. Remodeling of chromatin over the RNR3 promoter requires the recruitment of the SWI/SNF complex by the general transcription factor TFIID. We found that disrupting the nucleosome over the RNR3 core promoter relieves its dependence on TFIID and SWI/SNF, indicating a functional link between these two complexes. These results suggest that the specific function of TAF(II)s is to direct the chromatin remodeling step through SWI/SNF recruitment, and not core promoter selectivity. Our results indicate that nucleosome placement plays a dominant role in repression and that the ability of the core promoter to position a nucleosome is a major determinant in TAF(II) dependency of genes in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Han M, Grunstein M. Cell. 1988;55:1137–1145. - PubMed
-
- Wyrick JJ, Holstege FC, Jennings EG, Causton HC, Shore D, Grunstein M, Lander ES, Young RA. Nature. 1999;402:418–421. - PubMed
-
- Reinke H, Horz W. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1599–1607. - PubMed
-
- Boeger H, Griesenbeck J, Strattan JS, Kornberg RD. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1587–1598. - PubMed
-
- Lee CK, Shibata Y, Rao B, Strahl BD, Lieb JD. Nat Genet. 2004;36:900–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

