Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression
- PMID: 17502665
- PMCID: PMC2118603
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062512
Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression
Abstract
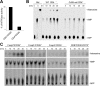
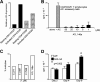
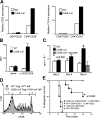
The study of T regulatory cells (T reg cells) has been limited by the lack of specific surface markers and an inability to define mechanisms of suppression. We show that the expression of CD39/ENTPD1 in concert with CD73/ecto-5'-nucleotidase distinguishes CD4(+)/CD25(+)/Foxp3(+) T reg cells from other T cells. These ectoenzymes generate pericellular adenosine from extracellular nucleotides. The coordinated expression of CD39/CD73 on T reg cells and the adenosine A2A receptor on activated T effector cells generates immunosuppressive loops, indicating roles in the inhibitory function of T reg cells. Consequently, T reg cells from Cd39-null mice show impaired suppressive properties in vitro and fail to block allograft rejection in vivo. We conclude that CD39 and CD73 are surface markers of T reg cells that impart a specific biochemical signature characterized by adenosine generation that has functional relevance for cellular immunoregulation.
Figures


References
-
- Sakaguchi, S., N. Sakaguchi, M. Asano, M. Itoh, and M. Toda. 1995. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Zheng, X.X., A. Sanchez-Fueyo, M. Sho, C. Domenig, M.H. Sayegh, and T.B. Strom. 2003. Favorably tipping the balance between cytopathic and regulatory T cells to create transplantation tolerance. Immunity. 19:503–514. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S. 2000. Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 101:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid, Y., and B.T. Rouse. 2005. Natural regulatory T cells in infectious disease. Nat. Immunol. 6:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Rouse, B.T., and S. Suvas. 2004. Regulatory cells and infectious agents: detentes cordiale and contraire. J. Immunol. 173:2211–2215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

