The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation
- PMID: 17502850
- PMCID: PMC2042938
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707264
The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation
Abstract
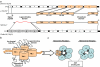
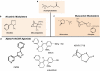
The physiological regulation of the immune system encompasses comprehensive anti-inflammatory mechanisms that can be harnessed for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory disorders. Recent studies indicate that the vagal nerve, involved in control of heart rate, hormone secretion and gastrointestinal motility, is also an immunomodulator. In experimental models of inflammatory diseases, vagal nerve stimulation attenuates the production of proinflammatory cytokines and inhibits the inflammatory process. Acetylcholine, the principal neurotransmitter of the vagal nerve, controls immune cell functions via the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7nAChR). From a pharmacological perspective, nicotinic agonists are more efficient than acetylcholine at inhibiting the inflammatory signaling and the production of proinflammatory cytokines. This 'nicotinic anti-inflammatory pathway' may have clinical implications as treatment with nicotinic agonists can modulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines from immune cells. Nicotine has been tested in clinical trials as a treatment for inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis, but the therapeutic potential of this mechanism is limited by the collateral toxicity of nicotine. Here, we review the recent advances that support the design of more specific receptor-selective nicotinic agonists that have anti-inflammatory effects while eluding its collateral toxicity.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham E, Anzueto A, Gutierrez G, Tessler S, San PG, Wunderink R, et al. Double-blind randomised controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumour necrosis factor in treatment of septic shock. vNORASEPT II Study Group. Lancet. 1998;351:929–933. - PubMed
-
- Aicher A, Heeschen C, Mohaupt M, Cooke JP, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Nicotine strongly activates dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immunity: potential role for progression of atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. 2003;107:604–611. - PubMed
-
- Aoshiba K, Nagai A, Yasui S, Konno K. Nicotine prolongs neutrophil survival by suppressing apoptosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1996;127:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Jolkovsky DL, Pinkerton KE, Grando SA. Receptor-mediated tobacco toxicity: cooperation of the Ras/Raf-1/MEK1/ERK and JAK-2/STAT-3 pathways downstream of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in oral keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2006;20:2093–2101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

