Early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) regulates HSV-1 ICP4 and ICP22 gene expression
- PMID: 17502875
- PMCID: PMC7092374
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2007.44
Early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) regulates HSV-1 ICP4 and ICP22 gene expression
Abstract
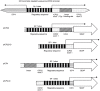
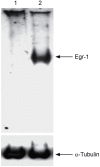
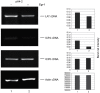
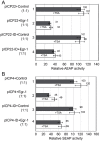
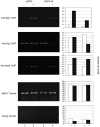
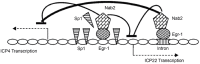
The molecular mechanisms mediating herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) gene silencing during latent infection are not clear. Five copies of early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) binding elements were identified in the intron of HSV-1 ICP22 (infected cell protein No. 22) gene, leading to the hypothesis that Egr-1 binds to the viral genome and regulates the viral gene expression. Transient co-transfection assays indicated that Egr-1 negatively regulated the transcription of both full-length and intron-removed ICP22 promoters. The same assays also revealed that Egr-1 repressed ICP4 (infected cell protein No. 4) promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner but showed less inhibition when the intron was removed. Histone deacetylation was not involved in this regulation since histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A did not exhibit any effect on Egr-1-mediated repression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that Egr-1 reduced the binding of Sp1 to the promoters and that the co-repressor Nab2 (NGFI-A/EGR1-binding protein) was recruited to the proximity of ICP4 in the presence of Egr-1. These results suggested that the multifunctional transcription factor Egr-1 can repress HSV-1 immediate-early gene expression through the recruitment of co-repressor Nab2 and reduction of Sp1 occupancy, and thus may play a critical role in HSV-1 gene silencing during latency.
Figures

References
-
- Peng W, Henderson G, Inman M. The locus encompassing the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 interferes with and delays interferon expression in productively infected neuroblastoma cells and trigeminal ganglia of acutely infected mice. J Virol. 2005;79:6162–6171. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.6162-6171.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM . In: Howley PM, Knipe DM, eds. Herpes simplex viruses and their replication from fundamental fields virology. 4th Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001: 2399–2460.
-
- Amelio AL, McAnany PK, Bloom DC. A chromatin insulator-like element in the herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript region binds CCCTC-binding factor and displays enhancer-blocking and silencing activities. J Virol. 2006;80:2358–2368. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.5.2358-2368.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

