A cyclin-dependent kinase that promotes cytokinesis through modulating phosphorylation of the carboxy terminal domain of the RNA Pol II Rpb1p sub-unit
- PMID: 17502918
- PMCID: PMC1855991
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000433
A cyclin-dependent kinase that promotes cytokinesis through modulating phosphorylation of the carboxy terminal domain of the RNA Pol II Rpb1p sub-unit
Abstract
In Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the nuclear-localized kinase, Lsk1p, promotes cytokinesis by positively regulating the Septation Initiation Network (SIN). Although a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) family, neither a cyclin partner nor a physiological target has been identified. In this report we identify a cyclin, Lsc1p, that physically interacts and co-localizes with Lsk1p. Furthermore, lsk1Delta, lsc1Delta, as well as kinase-dead lsk1-K306R mutants, display highly similar cytokinesis defects. Lsk1p is related to CDKs that phosphorylate the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest sub-unit of RNA polymerase II (Rpb1p). Interestingly, we find that Lsk1p and Lsc1p are required for phosphorylation of Ser-2 residues found in the heptad repeats of the CTD. To determine if Rpb1p could be a physiological target, we replaced the native rpb1 gene with a synthetic gene encoding a Rpb1p protein in which Ser-2 was substituted with the non-phosphorylatable amino-acid alanine in all heptads. Cells carrying this allele were similar to lsk1Delta mutants: They were viable, displayed genetic interactions with the SIN, and were unable to complete cytokinesis upon perturbation of the cell division machinery. We conclude that Ser-2 phosphorylation of the CTD heptads plays a novel physiological role in the regulation of cytokinesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
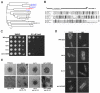

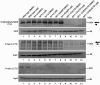
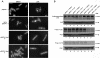

Similar articles
-
Global gene expression analysis of fission yeast mutants impaired in Ser-2 phosphorylation of the RNA pol II carboxy terminal domain.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024694. Epub 2011 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931816 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear kinase Lsk1p positively regulates the septation initiation network and promotes the successful completion of cytokinesis in response to perturbation of the actomyosin ring in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jan;16(1):358-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0502. Epub 2004 Nov 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15537703 Free PMC article.
-
The Medicago CDKC;1-CYCLINT;1 kinase complex phosphorylates the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II and promotes transcription.Plant J. 2005 Jun;42(6):810-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02421.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 15941395
-
Regulation of RNA polymerase II activity by CTD phosphorylation and cell cycle control.J Cell Physiol. 2002 Feb;190(2):160-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10058. J Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11807820 Review.
-
Modelling the CDK-dependent transcription cycle in fission yeast.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Dec;41(6):1660-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20130238. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 24256271 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A positive feedback loop links opposing functions of P-TEFb/Cdk9 and histone H2B ubiquitylation to regulate transcript elongation in fission yeast.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002822. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22876190 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain: Tethering transcription to transcript and template.Chem Rev. 2013 Nov 13;113(11):8423-55. doi: 10.1021/cr400158h. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 24040939 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Global gene expression analysis of fission yeast mutants impaired in Ser-2 phosphorylation of the RNA pol II carboxy terminal domain.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024694. Epub 2011 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931816 Free PMC article.
-
Individual letters of the RNA polymerase II CTD code govern distinct gene expression programs in fission yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Mar 18;111(11):4185-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321842111. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24591591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trautmann S, Wolfe BA, Jorgensen P, Tyers M, Gould KL, et al. Fission yeast Clp1p phosphatase regulates G2/M transition and coordination of cytokinesis with cell cycle progression. Curr Biol. 2001;11:931–940. - PubMed
-
- Mishra M, Karagiannis J, Sevugan M, Singh P, Balasubramanian MK. The 14-3-3 protein Rad24p modulates function of the Cdc14p family phosphatase Clp1p/Flp1p in fission yeast. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1376–1383. - PubMed
-
- Mishra M, Karagiannis J, Trautmann S, Wang H, McCollum D, et al. The Clp1p/Flp1p phosphatase ensures completion of cytokinesis in response to minor perturbation of the cell division machinery in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:3897–3910. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Wang H, Balasubramanian MK. A checkpoint that monitors cytokinesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1223–1230. - PubMed
-
- Le Goff X, Woollard A, Simanis V. Analysis of the cps1 gene provides evidence for a septation checkpoint in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1999;262:163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

