Gene copy-number variation and associated polymorphisms of complement component C4 in human systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): low copy number is a risk factor for and high copy number is a protective factor against SLE susceptibility in European Americans
- PMID: 17503323
- PMCID: PMC1867093
- DOI: 10.1086/518257
Gene copy-number variation and associated polymorphisms of complement component C4 in human systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): low copy number is a risk factor for and high copy number is a protective factor against SLE susceptibility in European Americans
Abstract
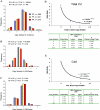
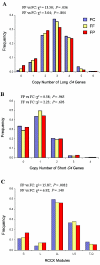
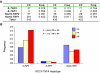
Interindividual gene copy-number variation (CNV) of complement component C4 and its associated polymorphisms in gene size (long and short) and protein isotypes (C4A and C4B) probably lead to different susceptibilities to autoimmune disease. We investigated the C4 gene CNV in 1,241 European Americans, including patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), their first-degree relatives, and unrelated healthy subjects, by definitive genotyping and phenotyping techniques. The gene copy number (GCN) varied from 2 to 6 for total C4, from 0 to 5 for C4A, and from 0 to 4 for C4B. Four copies of total C4, two copies of C4A, and two copies of C4B were the most common GCN counts, but each constituted only between one-half and three-quarters of the study populations. Long C4 genes were strongly correlated with C4A (R=0.695; P<.0001). Short C4 genes were correlated with C4B (R=0.437; P<.0001). In comparison with healthy subjects, patients with SLE clearly had the GCN of total C4 and C4A shifting to the lower side. The risk of SLE disease susceptibility significantly increased among subjects with only two copies of total C4 (patients 9.3%; unrelated controls 1.5%; odds ratio [OR] = 6.514; P=.00002) but decreased in those with > or =5 copies of C4 (patients 5.79%; controls 12%; OR=0.466; P=.016). Both zero copies (OR=5.267; P=.001) and one copy (OR=1.613; P=.022) of C4A were risk factors for SLE, whereas > or =3 copies of C4A appeared to be protective (OR=0.574; P=.012). Family-based association tests suggested that a specific haplotype with a single short C4B in tight linkage disequilibrium with the -308A allele of TNFA was more likely to be transmitted to patients with SLE. This work demonstrates how gene CNV and its related polymorphisms are associated with the susceptibility to a human complex disease.
Figures


References
Web Resources
-
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/ (for human genomic loci with possible gene CNV [build 36])
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for human C4A coding sequence [accession number NM_007293], human C4B coding sequence [accession number NM_001002029], human endogenous retrovirus in long C4 gene, HERV-K(C4) [accession number U07856], monomodular S RCCX coding for C4B [accession number AL662849], monomodular L RCCX coding for C4B [accession number NG_005163], and bimodular LL RCCX coding for C4B-C4A [accession number AL64592])
-
- International HapMap Project, http://www.hapmap.org/cgi-perl/gbrowse/hapmap_B35/
-
- MHC Haplotype Project, http://www.sanger.ac.uk/HGP/Chr6/MHC/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SLE, C4A, C4B, C1q, C1r, C1s, STK19, CYP21A1, TNXB, HLA-DRB1, HLA-B, and Ehlers-Danlo syndrome)
References
-
- Tsokos GC, Gordon C, Smolen JS (2007) Systemic lupus erythematosus: a companion to rheumatology. 1st ed. Mosby-Elsevier, Philadelphia
-
- Petri M (2006) Systemic lupus erythematosus and related diseases: clinical features. In: Rose NR, Mackay IR (eds) The autoimmune diseases. 4th ed. Elsevier Academic Press, St Louis, pp 351–356
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 HL70823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK055546/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050078/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR43814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL070823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043372/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR006009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR002248/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR2248/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5 P01 DK55546/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD43372/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1 P41 RR06009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR00046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01 AR050078/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

