Transcriptional control of SLC26A4 is involved in Pendred syndrome and nonsyndromic enlargement of vestibular aqueduct (DFNB4)
- PMID: 17503324
- PMCID: PMC1867094
- DOI: 10.1086/518314
Transcriptional control of SLC26A4 is involved in Pendred syndrome and nonsyndromic enlargement of vestibular aqueduct (DFNB4)
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Sep;81(3):634
Abstract
Although recessive mutations in the anion transporter gene SLC26A4 are known to be responsible for Pendred syndrome (PS) and nonsyndromic hearing loss associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct (EVA), also known as "DFNB4," a large percentage of patients with this phenotype lack mutations in the SLC26A4 coding region in one or both alleles. We have identified and characterized a key transcriptional regulatory element in the SLC26A4 promoter that binds FOXI1, a transcriptional activator of SLC26A4. In nine patients with PS or nonsyndromic EVA, a novel c.-103T-->C mutation in this regulatory element interferes with FOXI1 binding and completely abolishes FOXI1-mediated transcriptional activation. We have also identified six patients with mutations in FOXI1 that compromise its ability to activate SLC26A4 transcription. In one family, the EVA phenotype segregates in a double-heterozygous mode in the affected individual who carries single mutations in both SLC26A4 and FOXI1. This finding is consistent with our observation that EVA occurs in the Slc26a4(+/-); Foxi1(+/-) double-heterozygous mouse mutant. These results support a novel dosage-dependent model for the molecular pathogenesis of PS and nonsyndromic EVA that involves SLC26A4 and its transcriptional regulatory machinery.
Figures
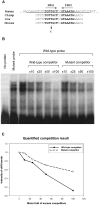
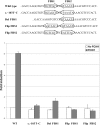

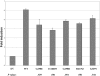
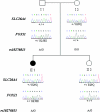

References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for SLC26A4 [accession number NC_000007.12], Slc26a4 [accession number NC_000078.4], Foxi1 [accession number NP_076396.2], FOXI1 [accession number NP_036320.2], Slc4a9 [accession number NC_000084.4], Atp6v1b1 [accession number NC_000072.4], SLC4A9 [accession number NC_000005.8], and ATP6V1B1 [accession number NC_000002.10])
-
- Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage, http://webh01.ua.ac.be/hhh/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.gov/Omim/ (for PS, SLC26A4, EVA, DFNB4, FOXI1, POU3F4, GJB2, Slc4a9, Atp6v1b1, FOXP2, EYA1, SIX1, BOR, EYA4, DFNA10, POU4F3, DFNA15, DFN3, GRHL2, DFNA28, PAX3, MITF, SNAI2, SOX10, WS1, WS2A, WS3, and WS4)
-
- UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway/ (for the genomic sequence alignment)
References
-
- Batsakis JG, Nishiyama RH (1962) Deafness with sporadic goiter: Pendred’s syndrome. Arch Otolaryngol 76:401–406 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

