Labeling biomolecules with radiorhenium: a review of the bifunctional chelators
- PMID: 17504162
- PMCID: PMC1949414
- DOI: 10.2174/187152007780618144
Labeling biomolecules with radiorhenium: a review of the bifunctional chelators
Abstract
For radiotherapy, biomolecules such as intact antibodies, antibody fragments, peptides, DNAs and other oligomers have all been labeled with radiorhenium ((186)Re and (188)Re). Three different approaches have been employed that may be referred to as direct, indirect and integral labeling. Direct labeling applies to proteins and involves the initial reduction of endogenous disulfide bridges to provide chelation sites. Indirect labeling can apply to most biomolecules and involves the initial attachment of an exogenous chelator. Finally, integral labeling is a special case applying only to small molecules in which the metallic radionuclide serves to link two parts of a biomolecule together in forming the labeled complex. While the number of varieties for the direct and integral radiolabeling approaches is rather limited, a fairly large and diverse number of chelators have been reported in the case of indirect labeling. Our objective herein is to provide an overview of the various chelators that have been used in the indirect labeling of biomolecules with radiorhenium, including details on the labeling procedures, the stability of the radiolabel and, where possible, the influence of the label on biological properties.
Figures
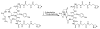
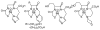
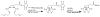
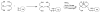
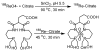
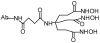
Similar articles
-
Monoclonal Antibodies Radiolabeling with Rhenium-188 for Radioimmunotherapy.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5923609. doi: 10.1155/2017/5923609. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28951872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhenium Radioisotopes for Medicine, a Focus on Production and Applications.Molecules. 2022 Aug 18;27(16):5283. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165283. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic and acyclic polyamines as chelators of rhenium-186 and rhenium-188 for therapeutic use.Nucl Med Biol. 1996 May;23(4):543-9. doi: 10.1016/0969-8051(96)00038-8. Nucl Med Biol. 1996. PMID: 8832713
-
Mixed tridentate π -donor and monodentate π -acceptor ligands as chelating systems for rhenium-188 and technetium-99m nitrido radiopharmaceuticals.Curr Radiopharm. 2013 Sep;6(3):137-45. doi: 10.2174/18744710113069990022. Curr Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 24106999
-
Single amino acid chelates (SAAC): a strategy for the design of technetium and rhenium radiopharmaceuticals.Chem Commun (Camb). 2009 Feb 7;(5):493-512. doi: 10.1039/b814903h. Epub 2008 Dec 1. Chem Commun (Camb). 2009. PMID: 19283279 Review.
Cited by
-
Bifunctional chelators for radiorhenium: past, present and future outlook.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Jan 14;13(3):217-245. doi: 10.1039/d1md00364j. eCollection 2022 Mar 23. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35434629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic and quantitative insight into cell surface targeted molecular imaging agent design.Sci Rep. 2016 May 5;6:25424. doi: 10.1038/srep25424. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27147293 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Synthesis of 99mTcN-Labeled Dextran-Mannose Derivatives for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Jul 16;11(3):70. doi: 10.3390/ph11030070. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30012952 Free PMC article.
-
188Re(V) Nitrido Radiopharmaceuticals for Radionuclide Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Jan 19;10(1):12. doi: 10.3390/ph10010012. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28106830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiolabeling strategies for tumor-targeting proteinaceous drugs.Molecules. 2014 Feb 18;19(2):2135-65. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022135. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24552984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miao Y, Owen NK, Whitener D, Gallazzi F, Hoffman TJ, Quinn TP. Int J Cancer. 2002;101:480. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Cheng Z, Miao Y, Jurisson SS, Quinn TP. Cancer. 2002;94(4 Suppl):1196. - PubMed
-
- Varnum JM, Thakur ML, Schally AV, Jansen S, Mayo KH. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:12583. - PubMed
-
- Iznaga-Escobar N. Appl Radiat Isot. 2001;54:399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

