Exon arrays provide accurate assessments of gene expression
- PMID: 17504534
- PMCID: PMC1929160
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-5-r82
Exon arrays provide accurate assessments of gene expression
Abstract
We have developed a strategy for estimating gene expression on Affymetrix Exon arrays. The method includes a probe-specific background correction and a probe selection strategy in which a subset of probes with highly correlated intensities across multiple samples are chosen to summarize gene expression. Our results demonstrate that the proposed background model offers improvements over the default Affymetrix background correction and that Exon arrays may provide more accurate measurements of gene expression than traditional 3' arrays.
Figures

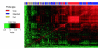
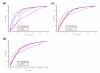
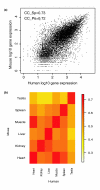
Similar articles
-
Probe selection and expression index computation of Affymetrix Exon Arrays.PLoS One. 2006 Dec 20;1(1):e88. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000088. PLoS One. 2006. PMID: 17183719 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the conservation of mammalian gene expression using high-density exon arrays.Mol Biol Evol. 2007 Jun;24(6):1283-5. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm061. Epub 2007 Mar 25. Mol Biol Evol. 2007. PMID: 17387099
-
Gene expression and isoform variation analysis using Affymetrix Exon Arrays.BMC Genomics. 2008 Nov 7;9:529. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-529. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18990248 Free PMC article.
-
Standards in gene expression microarray experiments.Methods Enzymol. 2006;411:63-78. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)11005-8. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16939786 Review.
-
Reliability and reproducibility issues in DNA microarray measurements.Trends Genet. 2006 Feb;22(2):101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.12.005. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Trends Genet. 2006. PMID: 16380191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Splice isoforms of phosducin-like protein control the expression of heterotrimeric G proteins.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):25760-25768. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.486258. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23888055 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of copy number variation and gene expression in neurofibromatosis type-1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours.Hum Genomics. 2015 Feb 15;9(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40246-015-0025-3. Hum Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25884485 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of TOP2A as a prognostic biomarker in patients with glioma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Mar 1;11(3):1228-1237. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of genetic variation contributing to differences in gene expression between populations.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Mar;82(3):631-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.015. Epub 2008 Feb 28. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18313023 Free PMC article.
-
Computational detection of alternative exon usage.Front Neurosci. 2011 May 13;5:69. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00069. eCollection 2011. Front Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21625610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affymetrix: Exon Array Design Datasheet http://www.affymetrix.com/support/technical/datasheets/exon_arraydesign_...
-
- Wu Z. A model-based background adjustment for oligonucleotide expression arrays. J Am Stat Assoc. 2004;99:909–917. doi: 10.1198/016214504000000683. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

