Immediate and short-term pain relief by acute sciatic nerve press: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 17504543
- PMCID: PMC1887521
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2253-7-4
Immediate and short-term pain relief by acute sciatic nerve press: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Despite much research, an immediately available, instantly effective and harmless pain relief technique has not been discovered. This study describes a new manipulation: a "2-minute sciatic nerve press", for rapid short-term relief of pain brought on by various dental and renal diseases.
Methods: This randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial ran in three hospitals in Anhui Province, China, with an enrollment of 66 out of 111 solicited patients aged 16 to 74 years. Patients were recruited sequentially, by specific participating physicians at their clinic visits to three independent hospitals. The diseases in enrolled dental patients included dental caries, periodontal diseases and dental trauma. Renal diseases in recruits included kidney infections, stones and some other conditions. Patients were randomly assigned to receive the "2-minute sciatic nerve press" or the "placebo press". For the "2-minute sciatic nerve press", pressure was applied simultaneously to the sciatic nerves at the back of the thighs, using the fists while patients lay prone. For the "placebo press", pressure was applied simultaneously to a parallel spot on the front of the thighs, using the fists while patients lay supine. Each fist applied a pressure of 11 to 20 kg for 2 minutes, after which, patients arose to rate pain.
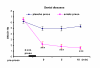
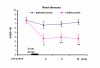
Results: The "2-minute sciatic nerve press" produced greater pain relief than the "placebo press". Within the first 10 minutes after sciatic pressure, immediate pain relief ratings averaged 66.4% (p < 0.001) for the dental patients, versus pain relief of 20% for the placebo press, and, 52.2% (p < 0.01) for the renal patients, versus relief of 14% for the placebo press, in median. The method worked excellently for dental caries and periodontal diseases, but poorly for dental trauma. Forty percent of renal patients with renal colic did not report any pain relief after the treatment.
Conclusion: Two minutes of pressure on both sciatic nerves can produce immediate significant conduction analgesia, providing a convenient, safe and powerful way to overcome clinical pain brought on by dental diseases and renal diseases for short term purposes.
Trial registration: ACTR 12606000439549.
Figures
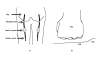
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

