A distance difference matrix approach to identifying transcription factors that regulate differential gene expression
- PMID: 17504544
- PMCID: PMC1929144
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-5-r83
A distance difference matrix approach to identifying transcription factors that regulate differential gene expression
Abstract
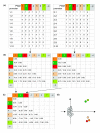
We introduce a method that considers target genes of a transcription factor, and searches for transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) of secondary factors responsible for differential responses among these targets. Based on the distance difference matrix concept, the method simultaneously integrates statistical overrepresentation and co-occurrence of TFBSs. Our approach is validated on datasets of differentially regulated human genes and is shown to be highly effective in detecting TFBSs responsible for the observed differential gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Berman BP, Nibu Y, Pfeiffer BD, Tomancak P, Celniker SE, Levine M, Rubin GM, Eisen MB. Exploiting transcription factor binding site clustering to identify cis-regulatory modules involved in pattern formation in the Drosophila genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:757–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.231608898. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

