Nucleosomes possess a high affinity for glomerular laminin and collagen IV and bind nephritogenic antibodies in murine lupus-like nephritis
- PMID: 17504842
- PMCID: PMC2095330
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.070482
Nucleosomes possess a high affinity for glomerular laminin and collagen IV and bind nephritogenic antibodies in murine lupus-like nephritis
Abstract
Aim: Lupus nephritis is closely associated with in vivo autoantibody-binding to glomerular membrane-associated electron-dense structures (EDS). The biochemical nature and cellular origin of EDS are controversial, and definitive characterisation needs to be performed.
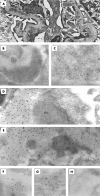
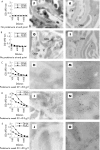
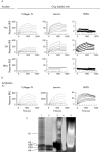
Methods: By using the terminal transferase biotin-dUTP nick end-labelling (TUNEL) assay at the electron microscopic level, we have traced extracellular chromatin within the glomerular basement membranes of nephritic (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. The TUNEL assay was subsequently used in combination with standard immune electron microscopy (IEM). To analyse why chromatin particles associate with membranes, we determined the affinity of nucleosomes and DNA for glomerular laminin, collagen IV and the mesangial matrix proteoglycan perlecan by surface plasmon resonance.
Results: This intra-assay colocalisation TUNEL IEM demonstrated that autoantibodies fully colocalised with extracellular TUNEL-positive chromatin observed as EDS in glomerular membranes, similar to results obtained by the same technique applied to human lupus nephritis. Most importantly, these data validate the murine variant of lupus nephritis as a model to study origin of extracellular chromatin as a key element in human lupus nephritis. Kinetic analyses demonstrated that nucleosomes had a high affinity for collagen IV and laminin, but not for perlecan.
Conclusion: Collectively, these results provide firm evidence that dominant target structures for nephritogenic autoantibodies are constituted by TUNEL-positive chromatin associated with glomerular capillary and mesangial matrix membranes at high affinity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Renal expression of polyomavirus large T antigen is associated with nephritis in human systemic lupus erythematosus.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jun;45(11):3117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.03.001. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18423862
-
Nephritogenic lupus antibodies recognize glomerular basement membrane-associated chromatin fragments released from apoptotic intraglomerular cells.Am J Pathol. 2006 Jun;168(6):1779-92. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051329. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16723695 Free PMC article.
-
Critical comparative analyses of anti-alpha-actinin and glomerulus-bound antibodies in human and murine lupus nephritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):914-26. doi: 10.1002/art.21622. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508974
-
A central role of nucleosomes in lupus nephritis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Jun;1108:104-13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1422.012. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17893976 Review.
-
Nephritogenic potential of anti-DNA antibodies against necrotic nucleosomes.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Apr;20(4):696-704. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008010112. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19329762 Review.
Cited by
-
Glomerular antibodies in lupus nephritis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;40(3):151-8. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8204-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20414746 Review.
-
Philosophical and distinct SLE epitomes: dogmas in conflict with evidences and an intellectual dissonance between established pathophysiological models.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1580664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1580664. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40777033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-dsDNA antibodies promote initiation, and acquired loss of renal Dnase1 promotes progression of lupus nephritis in autoimmune (NZBxNZW)F1 mice.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 29;4(12):e8474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008474. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20041189 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies: Focus on anti-DNA antibodies.Self Nonself. 2011 Jan;2(1):11-18. doi: 10.4161/self.2.1.15087. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Self Nonself. 2011. PMID: 21776330 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular matrix metalloproteinases and their regulators in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(6):229. doi: 10.1186/ar2532. Epub 2008 Dec 1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 19090960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hahn B H. Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med 19983381359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg D A, Ravirajan C T, Rahman A, Kalsi J. The role of antibodies to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus—a review and introduction to an international workshop on DNA antibodies held in London, May 1996. Lupus 19976290–304. - PubMed
-
- Balow J E, Boumpas D T, Austin III H A. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the kidney. In: Lahita RG, ed. Systemic lupus erythematosus. 4th ed. New York: Elsevier Academic Press, 2004877–912.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources