The effect of contact lens induced oedema on the accuracy of Goldmann tonometry in a mature population
- PMID: 17504854
- PMCID: PMC2095538
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2007.118695
The effect of contact lens induced oedema on the accuracy of Goldmann tonometry in a mature population
Abstract
Aim: To determine the effect of contact lens induced oedema on the accuracy of Goldmann tonometry measurements of intraocular pressure (IOP) in mature subjects.
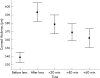
Methods: 22 healthy subjects aged between 50 and 60 years were recruited. Corneal curvature, IOP, and central corneal thickness (CCT) were measured before and after two hours of monocular closed eye wear of a thick hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) contact lens. Measurements were then repeated at 20 minute intervals for one hour after lens removal.
Results: Both CCT (+54.1 mum) and IOP (+2.7 mm Hg) increased significantly after lens wear (p<0.001, paired t test with Bonferroni correction). For the hour following lens removal, the measured IOP was correlated to the increase in CCT (r = 0.84, p<0.001), at a rate of 1.0 mm Hg/10 mum (95% confidence interval, 0.8 to 1.2 mm Hg/10 mum, linear mixed model analysis).
Conclusions: A relatively small increase in CCT from contact lens induced corneal oedema caused an overestimation error in Goldmann tonometry measurements of IOP in healthy mature subjects.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
The effect of contact lens induced corneal edema on Goldmann applanation tonometry measurements.J Glaucoma. 2007 Jan;16(1):153-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ijg.0000212277.95971.be. J Glaucoma. 2007. PMID: 17224766
-
The effect of corneal edema on dynamic contour and goldmann tonometry.Optom Vis Sci. 2008 Jun;85(6):451-6. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181783a86. Optom Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18521023
-
Determinants of postoperative corneal edema and impact on goldmann intraocular pressure.Cornea. 2011 Sep;30(9):962-7. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3182035884. Cornea. 2011. PMID: 21505325
-
Sources of error with use of Goldmann-type tonometers.Surv Ophthalmol. 1993 Jul-Aug;38(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(93)90053-a. Surv Ophthalmol. 1993. PMID: 8235993 Review.
-
Effects of contact lens-induced hypoxia on the physiology of the corneal endothelium.Optom Vis Sci. 2001 Nov;78(11):783-90. doi: 10.1097/00006324-200111000-00008. Optom Vis Sci. 2001. PMID: 11763252 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of contact lens-induced corneal edema on Goldmann applanation tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Mar;247(3):371-5. doi: 10.1007/s00417-008-0954-9. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 18843499
-
Effects of aging on corneal biomechanical properties and their impact on 24-hour measurement of intraocular pressure.Am J Ophthalmol. 2008 Oct;146(4):567-572. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.05.026. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18614134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Standards Organization ISO8612:2001(E): Ophthalmic instruments – tonometers. Geneva: ISO Copyright Office 2001
-
- Ehlers N, Bramsen T, Sperling S. Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 19755334–43. - PubMed
-
- Doughty M J, Zaman M L. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta‐analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol 200044367–408. - PubMed
-
- Whitacre M M, Stein R A, Hassanein K. The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 1993115592–596. - PubMed
-
- Mark H H. Corneal curvature in applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 197376223–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical