Effect of automated image registration on radiologist interpretation
- PMID: 17505869
- PMCID: PMC3043907
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-007-9023-x
Effect of automated image registration on radiologist interpretation
Abstract
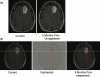
In this study, we present preliminary data on the effect of automated 3D image alignment on the time to arrive at a decision about an imaging finding, the agreement of multiple of multiple observers, the prevalence of comparison examinations, and technical success rates for the image alignment algorithm. We found that automated image alignment reduced the average time to make a decision by 25% for cases where the structures are rigid, and when the scanning protocol is similar. For cases where these are not true, there is little or no benefit. In our practice, 54% of cases had prior examinations that could be automatically aligned. The overall benefit seen in our department for highly similar exams might be 20% for neuro and 10% for body; the benefit seen in other practices is likely to vary based on scanning practices and prevalence of prior examinations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Digital image processing.Radiol Technol. 2004 Jul-Aug;75(6):435-52; quiz 453-5. Radiol Technol. 2004. PMID: 15352557
-
[Computation of mutual information in medical image registration based on mutual information].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Feb;25(1):12-7. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18435247 Chinese.
-
Image registration: an essential tool for nuclear medicine.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002 Apr;29(4):559-77. doi: 10.1007/s00259-001-0700-6. Epub 2002 Jan 11. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002. PMID: 11914898 Review.
-
F-information measures in medical image registration.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004 Dec;23(12):1508-16. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.836872. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004. PMID: 15575408
-
A review of 3D/2D registration methods for image-guided interventions.Med Image Anal. 2012 Apr;16(3):642-61. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Med Image Anal. 2012. PMID: 20452269 Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual Orientation Tools (VOTj): Fiji plugins for object centering and alignment.MicroPubl Biol. 2024 Jun 8;2024:10.17912/micropub.biology.001221. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001221. eCollection 2024. MicroPubl Biol. 2024. PMID: 38911438 Free PMC article.
-
Value of T1/T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging registration to reduce the postbiopsy hemorrhage effect for prostate cancer localization.Prostate Int. 2015 Sep;3(3):80-6. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Prostate Int. 2015. PMID: 26473149 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronized navigation of current and prior studies using image registration improves radiologist's efficiency.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017 Mar;12(3):431-438. doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1506-0. Epub 2016 Nov 26. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017. PMID: 27889861
-
Optimal presentation modes for detecting brain tumor progression.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Oct;32(9):1652-7. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2596. Epub 2011 Aug 18. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 21852368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collignon A, Maes F, Delaere D, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P, Marchal G. Automated multi-modality image registration based on information theory. In: Bizais YCB, Paola R, editors. Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Dodrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer; 1995. pp. 263–274.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

