Impaired spatial and non-spatial configural learning in patients with hippocampal pathology
- PMID: 17507060
- PMCID: PMC2572909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.04.007
Impaired spatial and non-spatial configural learning in patients with hippocampal pathology
Abstract
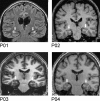
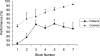
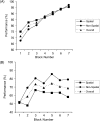
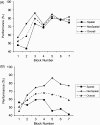
The hippocampus has been proposed to play a critical role in memory through its unique ability to bind together the disparate elements of an experience. This hypothesis has been widely examined in rodents using a class of tasks known as "configural" or "non-linear", where outcomes are determined by specific combinations of elements, rather than any single element alone. On the basis of equivocal evidence that hippocampal lesions impair performance on non-spatial configural tasks, it has been proposed that the hippocampus may only be critical for spatial configural learning. Surprisingly few studies in humans have examined the role of the hippocampus in solving configural problems. In particular, no previous study has directly assessed the human hippocampal contribution to non-spatial and spatial configural learning, the focus of the current study. Our results show that patients with primary damage to the hippocampus bilaterally were similarly impaired at configural learning within both spatial and non-spatial domains. Our data also provide evidence that residual configural learning can occur in the presence of significant hippocampal dysfunction. Moreover, evidence obtained from a post-experimental debriefing session suggested that patients acquired declarative knowledge of the underlying task contingencies that corresponded to the best-fit strategy identified by our strategy analysis. In summary, our findings support the notion that the hippocampus plays an important role in both spatial and non-spatial configural learning, and provide insights into the role of the medial temporal lobe (MTL) more generally in incremental reinforcement-driven learning.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A critical role for the hippocampus and perirhinal cortex in perceptual learning of scenes and faces: complementary findings from amnesia and FMRI.J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 19;33(25):10490-502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2958-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23785161 Free PMC article.
-
Fractionation of memory in medial temporal lobe amnesia.Neuropsychologia. 2007 Mar 25;45(6):1160-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.10.011. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Neuropsychologia. 2007. PMID: 17129591
-
A comparison of egocentric and allocentric spatial memory in medial temporal lobe and Korsakoff amnesics.Cortex. 1999 Sep;35(4):479-501. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(08)70814-1. Cortex. 1999. PMID: 10574076 Clinical Trial.
-
Structural learning and the hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2007;17(9):723-34. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20323. Hippocampus. 2007. PMID: 17598160 Review.
-
The neuroanatomy of amnesia. A critique of the hippocampal memory hypothesis.Brain. 1978 Sep;101(3):403-45. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.3.403. Brain. 1978. PMID: 101278 Review.
Cited by
-
Subtle Alterations in Spatial Memory Induced by Amyloid Peptides Infusion in Rats.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Jan 30;10:18. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29441014 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral toxicology of cognition: extrapolation from experimental animal models to humans: behavioral toxicology symposium overview.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012 Mar;34(2):263-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012. PMID: 22311110 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of bilateral hippocampal CA3 damage on the implicit learning and recognition of complex event sequences.Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Apr;15(2):27-55. doi: 10.1080/17588928.2024.2315818. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38384107 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Volume Reduction in Humans Predicts Impaired Allocentric Spatial Memory in Virtual-Reality Navigation.J Neurosci. 2015 Oct 21;35(42):14123-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0801-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26490854 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed bradykinin postconditioning modulates intrinsic neuroprotective enzyme expression in the rat CA1 region after cerebral ischemia: a proteomic study.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Dec;31(6):1391-1403. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9859-1. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 27393013
References
-
- Aggleton J.P., Vann S.D., Denby C., Dix S., Mayes A.R., Roberts N. Sparing of the familiarity component of recognition memory in a patient with hippocampal pathology. Neuropsychologia. 2005;43(12):1810–1823. - PubMed
-
- Alvarado M.C., Rudy J.W. Rats with damage to the hippocampal-formation are impaired on the transverse-patterning problem but not on elemental discriminations. Behavioral Neuroscience. 1995;109(2):204–211. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley A., Vargha-Khadem F., Mishkin M. Preserved recognition in a case of developmental amnesia: Implications for the acquisition of semantic memory? Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2001;13(3):357–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

