Lipid rafts of primary endothelial cells are essential for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and RhoA-GTPases critical for microtubule dynamics and nuclear delivery of viral DNA but dispensable for binding and entry
- PMID: 17507466
- PMCID: PMC1951274
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02848-06
Lipid rafts of primary endothelial cells are essential for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and RhoA-GTPases critical for microtubule dynamics and nuclear delivery of viral DNA but dispensable for binding and entry
Abstract
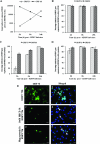
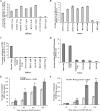
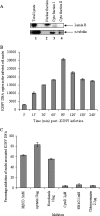
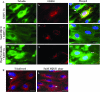
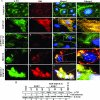
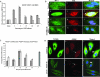
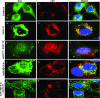
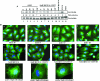
Early during de novo infection of human microvascular dermal endothelial (HMVEC-d) cells, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) (human herpesvirus 8 [HHV-8]) induces the host cell's preexisting FAK, Src, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K), Rho-GTPases, Diaphanous-2 (Dia-2), Ezrin, protein kinase C-zeta, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and NF-kappaB signal pathways that are critical for virus entry, nuclear delivery of viral DNA, and initiation of viral gene expression. Since several of these signal molecules are known to be associated with lipid raft (LR) domains, we investigated the role of LR during KSHV infection of HMVEC-d cells. Pretreatment of cells with LR-disrupting agents methyl beta-cyclo dextrin (MbetaCD) or nystatin significantly inhibited the expression of viral latent (ORF73) and lytic (ORF50) genes. LR disruption did not affect KSHV binding but increased viral DNA internalization. In contrast, association of internalized viral capsids with microtubules (MTs) and the quantity of infected nucleus-associated viral DNA were significantly reduced. Disorganized and disrupted MTs and thick rounded plasma membranes were observed in MbetaCD-treated cells. LR disruption did not affect KSHV-induced FAK and ERK1/2 phosphorylation; in contrast, it increased the phosphorylation of Src, significantly reduced the KSHV-induced PI3-K and RhoA-GTPase and NF-kappaB activation, and reduced the colocalizations of PI3-K and RhoA-GTPase with LRs. Biochemical characterization demonstrated the association of activated PI3-K with LR fractions which was inhibited by MbetaCD treatment. RhoA-GTPase activation was inhibited by PI3-K inhibitors, demonstrating that PI3-K is upstream to RhoA-GTPase. In addition, colocalization of Dia-2, a RhoA-GTPase activated molecule involved in MT activation, with LR was reduced. KSHV-RhoA-GTPase mediated acetylation and aggregation of MTs were also reduced. Taken together, these studies suggest that LRs of endothelial cells play critical roles in KSHV infection and gene expression, probably due to their roles in modulating KSHV-induced PI3-K, RhoA-GTPase, and Dia-2 molecules essential for postbinding and entry stages of infection such as modulation of microtubular dynamics, movement of virus in the cytoplasm, and nuclear delivery of viral DNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) early during infection of target cells are essential for expression of viral genes and for establishment of infection.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10308-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10308-10329.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051824 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA-GTPase facilitates entry of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus into adherent target cells in a Src-dependent manner.J Virol. 2006 Dec;80(23):11432-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01342-06. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 17005646 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus modulates microtubule dynamics via RhoA-GTP-diaphanous 2 signaling and utilizes the dynein motors to deliver its DNA to the nucleus.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(2):1191-206. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.2.1191-1206.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15613346 Free PMC article.
-
Early events in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection of target cells.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(5):2188-99. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01334-09. Epub 2009 Nov 18. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19923183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV Entry and Trafficking in Target Cells-Hijacking of Cell Signal Pathways, Actin and Membrane Dynamics.Viruses. 2016 Nov 14;8(11):305. doi: 10.3390/v8110305. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27854239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of the Tegument Proteins Involved in Capsid Transport and Virion Morphogenesis of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Herpesviruses.Viruses. 2023 Oct 6;15(10):2058. doi: 10.3390/v15102058. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37896835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho-GTPases subfamily: cellular defectors orchestrating viral infection.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 May 2;30(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00722-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40316910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initiation of human astrovirus type 1 infection was blocked by inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase.Virol J. 2013 May 16;10:153. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-153. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23680019 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of KSHV with host cell surface receptors and cell entry.Viruses. 2014 Oct 23;6(10):4024-46. doi: 10.3390/v6104024. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin 1 is an entry receptor for KSHV infection of mesenchymal stem cell through TGFBR1/2-mediated macropinocytosis.Sci Adv. 2023 May 24;9(21):eadg1778. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg1778. Epub 2023 May 24. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37224259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, S., J. Kim, C. L. Lucaveche, M. C. Reedy, L. M. Luttrell, R. J. Lefkowitz, and Y. Daaka. 2002. Src-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation regulates dynamin self-assembly and ligand-induced endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 277:26642-26651. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 envelope-associated glycoprotein B interacts with heparan sulfate-like moieties. Virology 284:235-249. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin α3β1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., F. Z. Wang, J. Vieira, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 interaction with target cells involves heparan sulfate. Virology 282:245-255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

