Rapid identification of Staphylococci isolated in clinical microbiology laboratories by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
- PMID: 17507519
- PMCID: PMC1932985
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02405-06
Rapid identification of Staphylococci isolated in clinical microbiology laboratories by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
Abstract
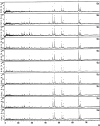
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) of intact bacteria yields a reproducible spectrum depending upon growth conditions, strain, or species. Using whole viable bacteria we describe here the application of MALDI-TOF-MS to the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). Our aim was, once a bacterium has been recognized as Micrococcaceae, to identify peaks in the spectrum that can be used to identify the species or subspecies. MALDI-TOF-MS was performed using bacteria obtained from one isolated colony. One reference strain for each of the 23 clinically relevant species or subspecies of Micrococcaceae was selected. For each reference strain, the MALDI-TOF-MS profile of 10 colonies obtained from 10 different passages was analyzed. For each strain, only peaks that were conserved in the spectra of all 10 isolated colonies and with a relative intensity above 0.1 were retained, thus leading to a set of 3 to 14 selected peaks per strain. The MALDI-TOF-MS profile of 196 tested strains was then compared with that of the set of selected peaks of each of the 23 reference strains. In all cases the best hit was with the set of peaks of the reference strain belonging to the same species as that of the tested strain, thus demonstrating that the 23 sets of selected peaks can be used as a database for the rapid species identification of CoNS. Similar results were obtained using four different growth conditions. Extending this strategy to other groups of relevant pathogenic bacteria will allow rapid bacterial identification.
Figures

References
-
- Andollina, A., A. De Cesare, G. Bertoni, L. Modeli, and G. Manfreda. 2004. Identification and genetic characterization of orthopaedic Staphylococcus isolates collected in Italy by automated EcoRI ribotyping. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 234:275-280. - PubMed
-
- Carretto, E., D. Barbarini, I. Couto, D. De Vitis, P. Marone, J. Verhoef, H. De Lencastre, and S. Brisse. 2005. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci other than Staphylococcus epidermidis by automated ribotyping. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 11:177-184. - PubMed
-
- Claydon, M. A., S. N. Davey, V. Edwards-Jones, and D. B. Gordon. 1996. The rapid identification of intact microorganisms using mass spectrometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 14:1584-1586. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

