Wnt-7a induces presynaptic colocalization of alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and adenomatous polyposis coli in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 17507554
- PMCID: PMC6672358
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3934-06.2007
Wnt-7a induces presynaptic colocalization of alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and adenomatous polyposis coli in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
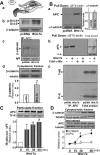
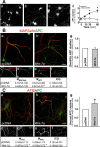
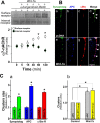
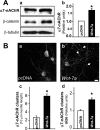
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) contribute significantly to hippocampal function. Alpha7-nAChRs are present in presynaptic sites in hippocampal neurons and may influence transmitter release, but the factors that determine their presynaptic localization are unknown. We report here that Wnt-7a, a ligand active in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, induces dissociation of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein from the beta-catenin cytoplasmic complex and the interaction of APC with alpha7-nAChRs in hippocampal neurons. Interestingly, Wnt-7a induces the relocalization of APC to membranes, clustering of APC in neurites, and coclustering of APC with different, presynaptic protein markers. Wnt-7a also increases the number and size of coclusters of alpha7-nAChRs and APC in presynaptic terminals. These short-term changes in alpha7-nAChRs occur in the few minutes after ligand exposure and involve translocation to the plasma membrane without affecting total receptor levels. Longer-term exposure to Wnt-7a increases nAChR alpha7 subunit levels in an APC-independent manner and increases clusters of alpha7-nAChRs in neurites via an APC-dependent process. Together, these results demonstrate that stimulation through the canonical Wnt pathway regulates the presynaptic localization of APC and alpha7-nAChRs with APC serving as an intermediary in the alpha7-nAChR relocalization process. Modulation by Wnt signaling may be essential for alpha7-nAChR expression and function in synapses.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nicotine prevents synaptic impairment induced by amyloid-β oligomers through α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Sep;15(3):549-69. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8242-1. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23842742
-
The postsynaptic adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) multiprotein complex is required for localizing neuroligin and neurexin to neuronal nicotinic synapses in vivo.J Neurosci. 2010 Aug 18;30(33):11073-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0983-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20720115 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-amyloid regulation of presynaptic nicotinic receptors in rat hippocampus and neocortex.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 30;23(17):6740-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06740.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12890766 Free PMC article.
-
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the hippocampal circuit: taming complexity.Trends Neurosci. 2022 Feb;45(2):145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Trends Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34916082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor and Wnt signaling in the regulation of apoptosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;656:75-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1145-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19928354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Wnt Signaling in Central Nervous System Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2297-311. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9138-x. Epub 2015 May 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25976365 Review.
-
LiCl attenuates impaired learning and memory of APP/PS1 mice, which in mechanism involves α7 nAChRs and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(22):10698-10710. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17006. Epub 2021 Oct 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34708522 Free PMC article.
-
Brain imaging of nicotinic receptors in Alzheimer's disease.Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2010 Dec 28;2010:548913. doi: 10.4061/2010/548913. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 21253523 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor-Cholesterol Crosstalk in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 11;14:744597. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.744597. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34803605 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's Disease and Protein Kinases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:285-321. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539020
References
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α7 and α4β2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:3043–3055. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez AR, Godoy JA, Mullendorff K, Olivares GH, Bronfman M, Inestrosa NC. Wnt-3a overcomes β-amyloid toxicity in rat hippocampal neurons. Exp Cell Res. 2004;297:186–196. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee C, Nyengaard JR, Wevers A, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Lindstrom J, Pilz K, Nowacki S, Bloch W, Schroder H. Cellular expression of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protein in the temporal cortex in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease—a stereological approach. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7:666–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
