Protein kinase C delta negatively regulates tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine synthesis by enhancing protein phosphatase-2A activity in dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 17507557
- PMCID: PMC3407040
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4107-06.2007
Protein kinase C delta negatively regulates tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine synthesis by enhancing protein phosphatase-2A activity in dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
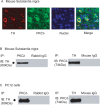
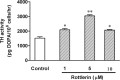
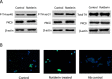
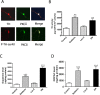
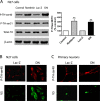
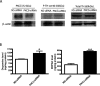
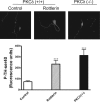
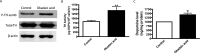
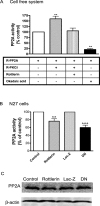
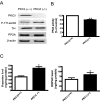
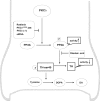
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate-limiting enzyme in dopamine synthesis, can be regulated by phosphorylation at multiple serine residues, including serine-40. In the present study, we report a novel interaction between a key member of the novel PKC family, protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta), and TH, in which the kinase modulates dopamine synthesis by negatively regulating TH activity via protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). We observed that PKCdelta is highly expressed in nigral dopaminergic neurons and colocalizes with TH. Interestingly, suppression of PKCdelta activity with the kinase inhibitor rottlerin, PKCdelta-small interfering RNA, or with PKCdelta dominant-negative mutant effectively increased a number of key biochemical events in the dopamine pathway, including TH-ser40 phosphorylation, TH enzymatic activity, and dopamine synthesis in neuronal cell culture models. Additionally, we found that PKCdelta not only physically associates with the PP2A catalytic subunit (PP2Ac) but also phosphorylates the phosphatase to increase its activity. Notably, inhibition of PKCdelta reduced the dephosphorylation activity of PP2A and thereby increased TH-ser40 phosphorylation, TH activity, and dopamine synthesis. To further validate our findings, we used the PKCdelta knock-out (PKCdelta-/-) mouse model. Consistent with other results, we found greater TH-ser40 phosphorylation and reduced PP2A activity in the substantia nigra of PKCdelta-/- mice than in wild-type mice. Importantly, this was accompanied by an increased dopamine level in the striatum of PKCdelta-/- mice. Collectively, these results suggest that PKCdelta phosphorylates PP2Ac to enhance its activity and thereby reduces TH-ser40 phosphorylation and TH activity and ultimately dopamine synthesis.
Figures

References
-
- Adams FS, La Rosa FG, Kumar S, Edwards-Prasad J, Kentroti S, Vernadakis A, Freed CR, Prasad KN. Characterization and transplantation of two neuronal cell lines with dopaminergic properties. Neurochem Res. 1996;21:619–627. - PubMed
-
- Anantharam V, Kitazawa M, Wagner J, Kaul S, Kanthasamy AG. Caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cdelta is essential for oxidative stress-mediated dopaminergic cell death after exposure to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl. J Neurosci. 2002;22:1738–1751. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bobrovskaya L, Cheah TB, Bunn SJ, Dunkley PR. Tyrosine hydroxylase in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: angiotensin II-stimulated activity and phosphorylation of Ser19, Ser31, and Ser40. J Neurochem. 1998;70:2565–2573. - PubMed
-
- Brodie C, Blumberg PM. Regulation of cell apoptosis by protein kinase c delta. Apoptosis. 2003;8:19–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
