Changes in synaptic morphology accompany actin signaling during LTP
- PMID: 17507558
- PMCID: PMC6672340
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0164-07.2007
Changes in synaptic morphology accompany actin signaling during LTP
Abstract
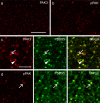
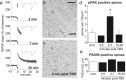
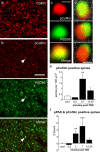
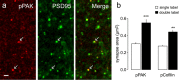
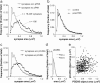
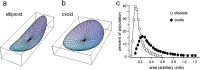
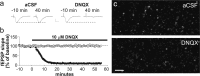
Stabilization of long-term potentiation (LTP) is commonly proposed to involve changes in synaptic morphology and reorganization of the spine cytoskeleton. Here we tested whether, as predicted from this hypothesis, induction of LTP by theta-burst stimulation activates an actin regulatory pathway and alters synapse morphology within the same dendritic spines. TBS increased severalfold the numbers of spines containing phosphorylated (p) p21-activated kinase (PAK) or its downstream target cofilin; the latter regulates actin filament assembly. The PAK/cofilin phosphoproteins were increased at 2 min but not 30 s post-TBS, peaked at 7 min, and then declined. Double immunostaining for the postsynaptic density protein PSD95 revealed that spines with high pPAK or pCofilin levels had larger synapses (+60-70%) with a more normal size frequency distribution than did neighboring spines. Based on these results and simulations of shape changes to synapse-like objects, we propose that theta stimulation markedly increases the probability that a spine will enter a state characterized by a large, ovoid synapse and that this morphology is important for expression and later stabilization of LTP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LTP enhances synaptogenesis in the developing hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2016 May;26(5):560-76. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22536. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26418237 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of size and number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses results in a balanced structural plasticity along mature hippocampal CA1 dendrites during LTP.Hippocampus. 2011 Apr;21(4):354-73. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20768. Hippocampus. 2011. PMID: 20101601 Free PMC article.
-
Remodelling of synaptic morphology but unchanged synaptic density during late phase long-term potentiation (LTP): a serial section electron micrograph study in the dentate gyrus in the anaesthetised rat.Neuroscience. 2004;128(2):251-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.029. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15350638
-
Rapid effects of oestrogen on synaptic plasticity: interactions with actin and its signalling proteins.J Neuroendocrinol. 2013 Nov;25(11):1163-72. doi: 10.1111/jne.12108. J Neuroendocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24112361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural LTP: Signal transduction, actin cytoskeleton reorganization, and membrane remodeling of dendritic spines.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;74:102534. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102534. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35398661 Review.
Cited by
-
ADF/cofilin: a crucial regulator of synapse physiology and behavior.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(18):3521-9. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1941-z. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26037722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cofilin Activation Is Temporally Associated with the Cessation of Growth in the Developing Hippocampus.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Apr 1;27(4):2640-2651. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw088. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 27073215 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of Genomic and Rapid Nongenomic Actions of Estrogens in Synaptic Plasticity.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):4113-4126. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9979-y. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27324789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal cord motor neuron plasticity accompanies second-degree burn injury and chronic pain.Physiol Rep. 2019 Dec;7(23):e14288. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14288. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31858746 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent dendritic spine shrinkage and growth involve downregulation of cofilin via distinct mechanisms.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 16;9(4):e94787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094787. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24740405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki C, Miko I, Oviedo H, Mikeladze-Dvali T, Alexandre L, Sweeney N, Bredt DS. Electron microscopic immunocytochemical detection of PSD-95, PSD-93, SAP-102, and SAP-97 at postsynaptic, presynaptic, and nonsynaptic sites of adult and neonatal rat visual cortex. Synapse. 2001;40:239–257. - PubMed
-
- Boda B, Nikonenko I, Alberi S, Muller D. Central nervous system functions of PAK protein family: from spine morphogenesis to mental retardation. Mol Neurobiol. 2006;34:67–80. - PubMed
