Connecting TNF-alpha signaling pathways to iNOS expression in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: relevance for the behavioral and synaptic deficits induced by amyloid beta protein
- PMID: 17507561
- PMCID: PMC6672347
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5047-06.2007
Connecting TNF-alpha signaling pathways to iNOS expression in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: relevance for the behavioral and synaptic deficits induced by amyloid beta protein
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Medeiros et al., "Connecting TNF-α Signaling Pathways to iNOS Expression in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease: Relevance for the Behavioral and Synaptic Deficits Induced by Amyloid β Protein".J Neurosci. 2021 Dec 8;41(49):10209-10210. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2000-21.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34789556 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
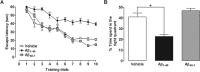
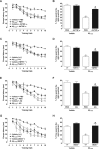
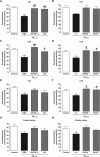
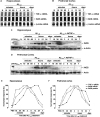
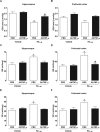
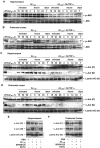
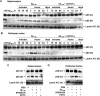
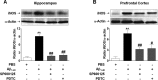
Increased brain deposition of amyloid beta protein (Abeta) and cognitive deficits are classical signals of Alzheimer's disease (AD) that have been highly associated with inflammatory alterations. The present work was designed to determine the correlation between tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-related signaling pathways and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in a mouse model of AD, by means of both in vivo and in vitro approaches. The intracerebroventricular injection of Abeta(1-40) in mice resulted in marked deficits of learning and memory, according to assessment in the water maze paradigm. This cognition impairment seems to be related to synapse dysfunction and glial cell activation. The pharmacological blockage of either TNF-alpha or iNOS reduced the cognitive deficit evoked by Abeta(1-40) in mice. Similar results were obtained in TNF-alpha receptor 1 and iNOS knock-out mice. Abeta(1-40) administration induced an increase in TNF-alpha expression and oxidative alterations in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Likewise, Abeta(1-40) led to activation of both JNK (c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase)/c-Jun and nuclear factor-kappaB, resulting in iNOS upregulation in both brain structures. The anti-TNF-alpha antibody reduced all of the molecular and biochemical alterations promoted by Abeta(1-40). These results provide new insights in mouse models of AD, revealing TNF-alpha and iNOS as central mediators of Abeta action. These pathways might be targeted for AD drug development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silibinin attenuates amyloid beta(25-35) peptide-induced memory impairments: implication of inducible nitric-oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Oct;331(1):319-26. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.155069. Epub 2009 Jul 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19638571
-
Imipramine, in part through tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition, prevents cognitive decline and beta-amyloid accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Feb;332(2):505-14. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.162164. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19889791
-
Restraining tumor necrosis factor-alpha by thalidomide prevents the amyloid beta-induced impairment of recognition memory in mice.Behav Brain Res. 2008 May 16;189(1):100-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.12.014. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Behav Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18325608
-
The Role of TNF-α in Alzheimer's Disease: A Narrative Review.Cells. 2023 Dec 26;13(1):54. doi: 10.3390/cells13010054. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated signaling in neuronal homeostasis and dysfunction.Cell Signal. 2010 Jul;22(7):977-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.010. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20096353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atorvastatin Prevents Cognitive Deficits Induced by Intracerebroventricular Amyloid-β1-40 Administration in Mice: Involvement of Glutamatergic and Antioxidant Systems.Neurotox Res. 2015 Jul;28(1):32-42. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9527-y. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Neurotox Res. 2015. PMID: 25827781
-
Targeting innate immunity for neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system.J Neurochem. 2016 Sep;138(5):653-93. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13667. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27248001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalidomide ameliorates portal hypertension via nitric oxide synthase independent reduced systolic blood pressure.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4126-35. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4126. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892862 Free PMC article.
-
The Learning Disabilities Network (LeaDNet): using neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) as a paradigm for translational research.Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Sep;158A(9):2225-32. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35535. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. PMID: 22821737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smad3-dependent signaling underlies the TGF-β1-mediated enhancement in astrocytic iNOS expression.Glia. 2010 Aug 15;58(11):1282-91. doi: 10.1002/glia.21005. Glia. 2010. PMID: 20607716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1072:129–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
