Monitoring synaptic function at the neuromuscular junction of a mouse expressing synaptopHluorin
- PMID: 17507564
- PMCID: PMC6672353
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0670-07.2007
Monitoring synaptic function at the neuromuscular junction of a mouse expressing synaptopHluorin
Abstract
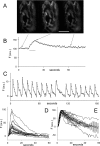
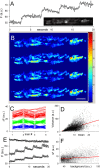
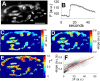
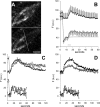
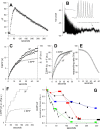
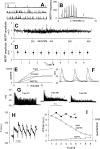
We monitored presynaptic exocytosis and vesicle recycling at neuromuscular junctions of transgenic mice expressing synaptopHluorin (spH), using simultaneous optical and electrophysiological recordings. Synaptic transmission was indistinguishable from that in wild-type controls. Fluorescence rose during and decayed monotonically after stimulus trains to the nerve, with amplitudes and decay times increasing with the amount of stimulation. The relatively large size of synaptic terminals allowed us to examine the spatial profile of fluorescence changes. We identified hot spots of exocytosis, which were stable with repeated trains. Photobleach experiments showed that spH freshly exposed by nerve stimulation was not preferentially retrieved by compensatory endocytosis; instead, most retrieved spH preexisted in the surface membrane. Finally, we compared fluorescence and electrical [summed end-plate potentials (EPPs)] estimates of exocytosis, which diverged during repeated trains, as fluorescence exceeded summed EPPs, although the average amplitude of miniature EPPs was unchanged. This might reflect exocytosis of spH-containing, acetylcholine-free ("empty") vesicles or other organelles during intense stimulation.
Figures
References
-
- Bozza T, McGann JP, Mombaerts P, Wachowiak M. In vivo imaging of neuronal activity by targeted expression of a genetically encoded probe in the mouse. Neuron. 2004;42:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Caroni P. Overexpression of growth-associated proteins in the neurons of adult transgenic mice. J Neurosci Methods. 1997;71:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Alfonso T, Kwan R, Ryan TA. Synaptic vesicles interchange their membrane proteins with a large surface reservoir during recycling. Neuron. 2006;51:179–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
