A fast, reciprocal pathway between the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex in the macaque monkey
- PMID: 17507565
- PMCID: PMC2888515
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1035-07.2007
A fast, reciprocal pathway between the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex in the macaque monkey
Abstract
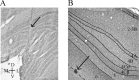
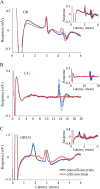
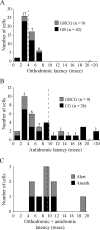
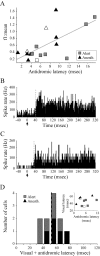
Neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) not only provide feedforward input to primary visual cortex (V1), but also receive robust feedback from the cortex. Accordingly, visual processing in the LGN is continuously influenced by previous patterns of activity. This study examines the temporal properties of feedforward and feedback pathways between the LGN and V1 in the macaque monkey to provide a lower bound on how quickly the cortex can influence the LGN. In so doing, we identified a subclass of corticogeniculate neurons that receives direct, suprathreshold input from the LGN that is similar in latency to that directed to other recipient neurons (4.2 +/- 0.4 vs 4.0 +/- 0.2 ms). These neurons also provide feedback to the LGN that is significantly shorter in latency than that supplied by corticogeniculate neurons lacking LGN input (5.1 +/- 1.3 vs 11.1 +/- 2.3 ms, respectively). Across our sample of corticogeniculate neurons, the shortest combined visual response latency and feedback latency was 37 ms (mean, 52.5 +/- 3.8 ms), indicating that visual signals can rapidly travel from the periphery to the cortex and back to the LGN.
Figures
References
-
- Alitto HJ, Usrey WM. Corticothalamic feedback and sensory processing. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Briggs F, Usrey WM. Encyclopedia of neuroscience. Ed 4. Elsevier; 2007. Corticothalamic circuits: structure and function. in press.
-
- Bullier J, Henry GH. Ordinal position and afferent input of neurons in monkey striate cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1980;193:913–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
