Ets-2 repressor factor silences extrasynaptic utrophin by N-box mediated repression in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 17507653
- PMCID: PMC1949368
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-12-1069
Ets-2 repressor factor silences extrasynaptic utrophin by N-box mediated repression in skeletal muscle
Abstract
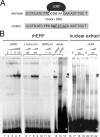
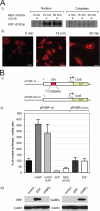
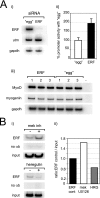
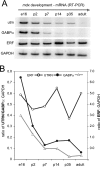
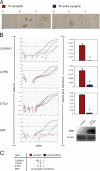
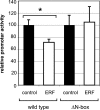
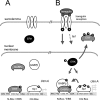
Utrophin is the autosomal homologue of dystrophin, the protein product of the Duchenne's muscular dystrophy (DMD) locus. Utrophin expression is temporally and spatially regulated being developmentally down-regulated perinatally and enriched at neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) in adult muscle. Synaptic localization of utrophin occurs in part by heregulin-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-phosphorylation, leading to binding of GABPalpha/beta to the N-box/EBS and activation of the major utrophin promoter-A expressed in myofibers. However, molecular mechanisms contributing to concurrent extrasynaptic silencing that must occur to achieve NMJ localization are unknown. We demonstrate that the Ets-2 repressor factor (ERF) represses extrasynaptic utrophin-A in muscle. Gel shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation studies demonstrated physical association of ERF with the utrophin-A promoter N-box/EBS site. ERF overexpression repressed utrophin-A promoter activity; conversely, small interfering RNA-mediated ERF knockdown enhanced promoter activity as well as endogenous utrophin mRNA levels in cultured muscle cells in vitro. Laser-capture microscopy of tibialis anterior NMJ and extrasynaptic transcriptomes and gene transfer studies provide spatial and direct evidence, respectively, for ERF-mediated utrophin repression in vivo. Together, these studies suggest "repressing repressors" as a potential strategy for achieving utrophin up-regulation in DMD, and they provide a model for utrophin-A regulation in muscle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of utrophin promoter by heregulin via the ets-related transcription factor complex GA-binding protein alpha/beta.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jun;10(6):2075-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.6.2075. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10359616 Free PMC article.
-
Sp1 and the ets-related transcription factor complex GABP alpha/beta functionally cooperate to activate the utrophin promoter.J Neurol Sci. 2002 May 15;197(1-2):27-35. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00038-2. J Neurol Sci. 2002. PMID: 11997063
-
Heregulin-induced epigenetic regulation of the utrophin-A promoter.FEBS Lett. 2007 Sep 4;581(22):4153-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.021. Epub 2007 Jul 23. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17692845 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple regulatory events controlling the expression and localization of utrophin in skeletal muscle fibers: insights into a therapeutic strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Physiol Paris. 2002 Jan-Mar;96(1-2):31-42. doi: 10.1016/s0928-4257(01)00078-x. J Physiol Paris. 2002. PMID: 11755781 Review.
-
Regulation and functional significance of utrophin expression at the mammalian neuromuscular synapse.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Apr 1;49(1):90-100. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(20000401)49:1<90::AID-JEMT10>3.0.CO;2-L. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10757882 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous bioluminescent reporters reveal a sustained increase in utrophin gene expression upon EZH2 and ERK1/2 inhibition.Commun Biol. 2023 Mar 25;6(1):318. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04666-9. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36966198 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of utrophin and dystrophin combination therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Jul 1;28(13):2189-2200. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz049. Hum Mol Genet. 2019. PMID: 30990876 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation of utrophin by miRNAs.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029376. Epub 2011 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22216264 Free PMC article.
-
Novel adeno-associated viral vector delivering the utrophin gene regulator jazz counteracts dystrophic pathology in mdx mice.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Sep;229(9):1283-91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24567. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24469912 Free PMC article.
-
UtroUp is a novel six zinc finger artificial transcription factor that recognises 18 base pairs of the utrophin promoter and efficiently drives utrophin upregulation.BMC Mol Biol. 2013 Jan 30;14:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-14-3. BMC Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23363418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballas N., et al. Regulation of neuronal traits by a novel transcriptional complex. Neuron. 2001;31:353–365. - PubMed
-
- Budak M. T., Bogdanovich S., Wiesen M. H., Lozynska O., Khurana T. S., Rubinstein N. A. Layer-specific differences of gene expression in extraocular muscles identified by laser-capture microscopy. Physiol. Genomics. 2004;20:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Cerletti M., et al. Dystrophic phenotype of canine X-linked muscular dystrophy is mitigated by adenovirus-mediated utrophin gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2003;10:750–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

