Epstein Barr virus specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing the anti-CD30zeta artificial chimeric T-cell receptor for immunotherapy of Hodgkin disease
- PMID: 17507664
- PMCID: PMC1988944
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-059139
Epstein Barr virus specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing the anti-CD30zeta artificial chimeric T-cell receptor for immunotherapy of Hodgkin disease
Abstract
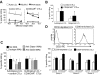
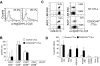
Adoptive transfer of Epstein Barr virus (EBV)-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (EBV-CTLs) has shown that these cells persist in patients with EBV(+) Hodgkin lymphoma (HD) to produce complete tumor responses. Treatment failure, however, occurs if a subpopulation of malignant cells in the tumor lacks or loses expression of EBV antigens. We have therefore determined whether we could prepare EBV-CTLs that retained the antitumor activity conferred by their native receptor while expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific for CD30, a molecule highly and consistently expressed on malignant Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells. We made a CD30CAR and were able to express it on 26% (+/- 11%) and 22% (+/- 5%) of EBV-CTLs generated from healthy donors and HD patients, respectively. These CD30CAR(+) CTLs killed both autologous EBV(+) cells through their native receptor and EBV(-)/CD30(+) targets through their major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-unrestricted CAR. A subpopulation of activated T cells also express CD30, but the CD30CAR(+) CTLs did not impair cellular immune responses, probably because normal T cells express lower levels of the target antigen. In a xenograft model, CD30CAR(+) EBV-CTLs could be costimulated by EBV-infected cells and produce antitumor effects even against EBV(-)/CD30(+) tumors. EBV-CTLs expressing both a native and a chimeric antigen receptor may therefore have added value for treatment of HD.
Figures
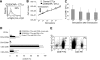
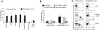



References
-
- Yung L, Linch D. Hodgkin's lymphoma. Lancet. 2003;361:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Aleman BM, Raemaekers JM, Tirelli U, et al. Involved-field radiotherapy for advanced Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2396–2406. - PubMed
-
- Diehl V, Franklin J, Pfreundschuh M, et al. Standard and increased-dose BEACOPP chemotherapy compared with COPP-ABVD for advanced Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2386–2395. - PubMed
-
- Ng AK, Mauch PM. Late complications of therapy of Hodgkin's disease: prevention and management. Curr Hematol Rep. 2004;3:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Wu TC, Mann RB, Charache P, et al. Detection of EBV gene expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1990;46:801–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

