Regional control of chromatin organization by noncoding roX RNAs and the NURF remodeling complex in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 17507677
- PMCID: PMC1931522
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.071571
Regional control of chromatin organization by noncoding roX RNAs and the NURF remodeling complex in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
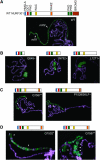
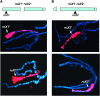
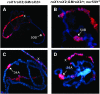
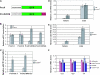
Dosage compensation in Drosophila is mediated by a histone-modifying complex that upregulates transcription of genes on the single male X chromosome. The male-specific lethal (MSL) complex contains at least five proteins and two noncoding roX (RNA on X) RNAs. The mechanism by which the MSL complex targets the X chromosome is not understood. Here we use a sensitized system to examine the function of roX genes on the X chromosome. In mutants that lack the NURF nucleosome remodeling complex, the male polytene X chromosome is severely distorted, appearing decondensed. This aberrant morphology is dependent on the MSL complex. Strikingly, roX mutations suppress the Nurf mutant phenotype regionally on the male X chromosome. Furthermore, a roX transgene induces disruption of local flanking autosomal chromatin in Nurf mutants. Taken together, these results demonstrate the potent capability of roX genes to organize large chromatin domains in cis, on the X chromosome. In addition to interacting functions at the level of chromosome morphology, we also find that NURF complex and MSL proteins have opposing effects on roX RNA transcription. Together, these results demonstrate the importance of a local balance between modifying activities that promote and antagonize chromatin compaction within defined chromatin domains in higher organisms.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

