Locating multiple interacting quantitative trait Loci using rank-based model selection
- PMID: 17507685
- PMCID: PMC1931563
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.068031
Locating multiple interacting quantitative trait Loci using rank-based model selection
Abstract
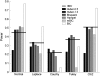
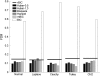
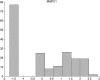
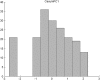
In previous work, a modified version of the Bayesian information criterion (mBIC) was proposed to locate multiple interacting quantitative trait loci (QTL). Simulation studies and real data analysis demonstrate good properties of the mBIC in situations where the error distribution is approximately normal. However, as with other standard techniques of QTL mapping, the performance of the mBIC strongly deteriorates when the trait distribution is heavy tailed or when the data contain a significant proportion of outliers. In the present article, we propose a suitable robust version of the mBIC that is based on ranks. We investigate the properties of the resulting method on the basis of theoretical calculations, computer simulations, and a real data analysis. Our simulation results show that for the sample sizes typically used in QTL mapping, the methods based on ranks are almost as efficient as standard techniques when the data are normal and are much better when the data come from some heavy-tailed distribution or include a proportion of outliers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extending the modified bayesian information criterion (mBIC) to dense markers and multiple interval mapping.Biometrics. 2008 Dec;64(4):1162-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2008.00989.x. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Biometrics. 2008. PMID: 18266892
-
On locating multiple interacting quantitative trait loci in intercross designs.Genetics. 2006 Jul;173(3):1693-703. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.048108. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16624924 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the Schwarz Bayesian information criterion to locate multiple interacting quantitative trait loci.Genetics. 2004 Jun;167(2):989-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.103.021683. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15238547 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection.Theor Appl Genet. 2012 Aug;125(3):419-35. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1892-9. Epub 2012 May 24. Theor Appl Genet. 2012. PMID: 22622521 Review.
-
Current progress on statistical methods for mapping quantitative trait loci from inbred line crosses.J Biopharm Stat. 2010 Mar;20(2):454-81. doi: 10.1080/10543400903572845. J Biopharm Stat. 2010. PMID: 20309768 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the genetic characteristics of two recombinant inbred line populations via high-density SNP markers in maize.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052777. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300772 Free PMC article.
-
A two-phase procedure for QTL mapping with regression models.Theor Appl Genet. 2010 Jul;121(2):363-72. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1315-8. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Theor Appl Genet. 2010. PMID: 20336448
-
Adaptive modelling of gene regulatory network using Bayesian information criterion-guided sparse regression approach.IET Syst Biol. 2016 Dec;10(6):252-259. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2016.0005. IET Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 27879480 Free PMC article.
-
Rank-based inverse normal transformations are increasingly used, but are they merited?Behav Genet. 2009 Sep;39(5):580-95. doi: 10.1007/s10519-009-9281-0. Epub 2009 Jun 14. Behav Genet. 2009. PMID: 19526352 Free PMC article.
-
Selecting predictive biomarkers from genomic data.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 16;17(6):e0269369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269369. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35709188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike, H., 1974. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 19: 716–723.
-
- Baierl, A., A. Futschik, M. Bogdan and P. Biecek, 2007. Locating multiple interacting quantitative trait loci using robust model selection. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/01679473) (in press). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y., and Y. Hochberg, 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 57: 289–300.
-
- Bogdan, M., and R. W. Doerge, 2005. Biased estimators of quantitative trait locus heritability and location in interval mapping. Heredity 95: 476–484. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

