E2F4 function in G2: maintaining G2-arrest to prevent mitotic entry with damaged DNA
- PMID: 17507799
- PMCID: PMC2596058
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.6.10.4259
E2F4 function in G2: maintaining G2-arrest to prevent mitotic entry with damaged DNA
Abstract
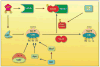
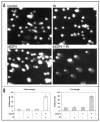
Mammalian cells undergo cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage through multiple checkpoint mechanisms. One such checkpoint pathway maintains genomic integrity by delaying mitotic progression in response to genotoxic stress. Transition though the G2 phase and entry into mitosis is considered to be regulated primarily by cyclin B1 and its associated catalytically active partner Cdk1. While not necessary for its initiation, the p130 and Rb-dependent target genes have emerged as being important for stable maintenance of a G2 arrest. It was recently demonstrated that by interacting with p130, E2F4 is present in the nuclei and plays a key role in the maintenance of this stable G2 arrest. Increased E2F4 levels and its translocation to the nucleus following genotoxic stress result in downregulation of many mitotic genes and as a result promote a G0-like state. Irradiation of E2F4-depleted cells leads to enhanced cellular DNA double-strand breaks that may be measured by comet assays. It also results in cell death that is characterized by caspase activation, sub-G1 and sub-G2 DNA content, and decreased clonogenic cell survival. Here we review these recent findings and discuss the mechanisms of G2 phase checkpoint activation and maintenance with a particular focus on E2F4.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
