The diverse functions of Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology
- PMID: 17508399
- PMCID: PMC2211634
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.20581
The diverse functions of Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology
Erratum in
- Bioessays. 2007 Sep;29(9):946
Abstract
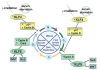
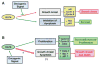
The Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) comprise a family of evolutionarily conserved zinc finger transcription factors that regulate numerous biological processes including proliferation, differentiation, development and apoptosis. KLF4 and KLF5 are two closely related members of this family and are both highly expressed in epithelial tissues. In the intestinal epithelium, KLF4 is expressed in terminally differentiated epithelial cells at the villus borders of the mucosa and inhibits cell growth, while KLF5 is expressed in proliferating epithelial cells at the base of the intestinal crypts and promotes cell growth. KLF4 and KLF5 respond to a myriad of external stress stimuli and are likely involved in restoring cellular homeostasis following exposure to stressors. Confirming their importance in maintaining tissue integrity, KLF4 and KLF5 are both dysregulated in various types of cancer. Here we review the recent advances in defining the physiological and pathobiological roles of KLF4 and KLF5, focusing on their functions in the intestinal epithelium.
(c) 2007 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
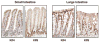
References
-
- Jackle H, Rosenberg UB, Preiss A, Seifert E, Knipple DC, et al. Molecular analysis of Kruppel, a segmentation gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:465–473. - PubMed
-
- Preiss A, Rosenberg UB, Kienlin A, Seifert E, Jackle H. Molecular genetics of Krüppel, a gene required for segmentation of the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1985;313:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Wieschaus E, Nusslein-Volhard C, Kluding H. Krüppel, a gene whose activity is required early in the zygotic genome for normal embryonic segmentation. Dev Biol. 1984;104:172–186. - PubMed
-
- Bieker JJ. Kruppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:34355–34358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

