MUC1 is involved in trophoblast transendothelial migration
- PMID: 17509701
- PMCID: PMC1986703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.04.006
MUC1 is involved in trophoblast transendothelial migration
Abstract
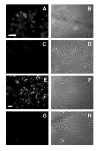
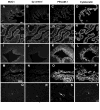
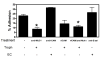
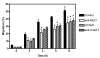
The factors that regulate trophoblast invasion of the uterine vasculature are incompletely understood. In this paper we show that macaque trophoblasts express the mucin, MUC1, and that it is involved in trophoblast-endothelial interaction. Immunocytochemistry, Western blotting and RT-PCR analyses confirmed that MUC1 was expressed by isolated early gestation macaque trophoblasts. MUC1 was also detected in endovascular trophoblasts in sections of placental-decidual tissue during early gestation. A blocking antibody against MUC1 reduced trophoblast adhesion to uterine endothelial cells and also blocked trophoblast transendothelial migration. MUC1 is known to bind to Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in other systems. Incubation in the presence of a blocking antibody against Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) or recombinant ICAM-1 modestly, but significantly, reduced transendothelial trophoblast migration. These results are consistent with the idea that MUC1 is involved in trophoblast adhesion to uterine endothelial cells and in trophoblast transendothelial migration.
Figures

References
-
- Gendler SJ. MUC1, the renaissance molecule. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2001;6:339–53. - PubMed
-
- Cloosen S, Thio M, Vanclee A, van Leeuwen EB, Senden-Gijsbers BL, Oving EB, Germeraad WT, Bos GM. Mucin-1 is expressed on dendritic cells, both in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunol. 2004;16:1561–71. - PubMed
-
- Wykes M, MacDonald KP, Tran M, Quin RJ, Xing PX, Gendler SJ, Hart DN, McGuckin MA. MUC1 epithelial mucin (CD227) is expressed by activated dendritic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72:692–701. - PubMed
-
- Hilkens J, Wesseling J, Vos HL, Storm J, Boer B, van der Valk SW, Maas MC. Involvement of the cell surface-bound mucin, episialin/MUC1, in progression of human carcinomas. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995;23:822–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

