Influence of XPB helicase on recruitment and redistribution of nucleotide excision repair proteins at sites of UV-induced DNA damage
- PMID: 17509950
- PMCID: PMC3471374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.03.025
Influence of XPB helicase on recruitment and redistribution of nucleotide excision repair proteins at sites of UV-induced DNA damage
Abstract
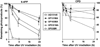
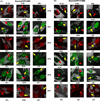
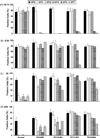
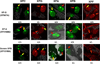
The XPB DNA helicase, a subunit of the basal transcription factor TFIIH, is also involved in nucleotide excision repair (NER). We examined recruitment of NER proteins in XP-B cells from patients with mild or severe xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) having different XPB mutations using local UV-irradiation through filters with 5 microm pores combined with fluorescent antibody labeling. XPC was rapidly recruited to UV damage sites containing DNA photoproducts (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, CPD) in all the XP-B and normal cells, thus reflecting its role in damage recognition prior to the function of XPB. Cells from the mild XP-B patients, with a missense mutation, showed delayed recruitment of all NER proteins except XPC to UV damage sites, demonstrating that this mutation impaired localization of these proteins. Surprisingly, in cells from severely affected patients, with a C-terminal XPB mutation, XPG and XPA proteins were normally recruited to UV damage sites demonstrating that this mutation permits recruitment of XPG and XPA. In marked contrast, in all the XP-B cells recruitment of XPF was absent immediately after UV and was delayed by 0.5 and 3 h in cells from the mild and severely affected XP patients, respectively. Redistribution of NER proteins was nearly complete in normal cells by 3 h but by 24 h redistribution was only partially present in cells from mild patients and virtually absent in cells from the severely affected patients. Ineffectual repair of UV-induced photoproducts resulting from delayed recruitment and impaired redistribution of NER proteins may contribute to the markedly increased frequency of skin cancer in XP patients.
Figures

References
-
- Bootsma D, Kraemer KH, Cleaver JE, Hoeijmakers JHJ. Nucleotide excision repair syndromes: xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne syndrome, and trichothiodystrophy. In: Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, editors. The Genetic Basis of Human Cancer. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2002. pp. 211–237.
-
- Lindahl T, Wood RD. Quality control by DNA repair. Science. 1999;286:1897–1905. - PubMed
-
- Moriwaki S, Kraemer KH. Xeroderma pigmentosum—bridging a gap between clinic and laboratory. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2001;17:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2006.
-
- Petit C, Sancar A. Nucleotide excision repair: from E. coli to man. Biochimie. 1999;81:15–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

