Adenoviral vectors persist in vivo and maintain activated CD8+ T cells: implications for their use as vaccines
- PMID: 17510320
- PMCID: PMC1976365
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-062117
Adenoviral vectors persist in vivo and maintain activated CD8+ T cells: implications for their use as vaccines
Abstract
CD8(+) T cell-numbers rapidly expand and then contract after exposure to their cognate antigen. Here we show that the sustained frequencies of transgene product-specific CD8(+) T cells elicited by replication-defective adenovirus vectors are linked to persistence of low levels of transcriptionally active adenovirus vector genomes at the site of inoculation, in liver, and lymphatic tissues. Continuously produced small amounts of antigen maintain fully active effector CD8(+) T cells, while also allowing for their differentiation into central memory cells. The long-term persistence of adenoviral vectors may be highly advantageous for their use as vaccines against pathogens for which T-cell-mediated protection requires both fully activated T cells for immediate control of virus-infected cells and central memory CD8(+) T cells that, because of their higher proliferative capacity, may be suited best to eliminate cells infected by pathogens that escaped the initial wave of effector T cells.
Figures


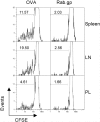


References
-
- McMichael AJ. HIV vaccines. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:227–255. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. HIV/AIDS. Hedged bet: an unusual AIDS vaccine trial. Science. 2005;309:1003. - PubMed
-
- Schultz AM, Bradac JA. The HIV vaccine pipeline, from preclinical to phase III. AIDS. 2001;15(Suppl 5):S147–158. - PubMed
-
- Shiver JW, Emini EA. Recent advances in the development of HIV-1 vaccines using replication-incompetent adenovirus vectors. Annu Rev Med. 2004;55:355–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

