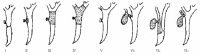Bile duct injuries associated with laparoscopic and open cholecystectomy: sixteen-year experience
- PMID: 17511041
- PMCID: PMC4147151
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i16.2374
Bile duct injuries associated with laparoscopic and open cholecystectomy: sixteen-year experience
Abstract
Aim: To summarize the experience in diagnosis, management and prevention of iatrogenic bile duct injury (IBDI).
Methods: A total of 210 patients with bile duct injury occurred during cholecystectomy admitted to Hunan Provincial People's Hospital from March 1990 to March 2006 were included in this study for retrospective analysis.
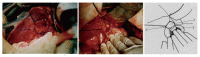
Results: There were 59.5% (103/173) of patients with IBDI resulting from the wrong identification of the anatomy of the Calot's triangle during cholecystectomy. The diagnosis of IBDI was made on the basis of clinical features, diagnostic abdominocentesis and imaging findings. Abdominal B ultrasonography (BUS) was the most popular way for IBDI with a diagnostic rate of 84.6% (126/149). Magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC) could reveal the site of injury, the length of injured bile duct and variation of bile duct tree with a diagnostic rate 100% (45/45). According to the site of injury, IBDI could be divided into six types. The most common type (type 3) occurred in 76.7% (161/210) of the patients and was treated with partial resection of the common hepatic duct and common bile duct. One hundred and seventy-six patients were followed up. The mean follow-up time was 3.7 (range 0.25-10) years. Good results were achieved in 87.5% (154/176) of the patients.
Conclusion: The key to prevention of IBDI is to follow the "identifying-cutting-identifying" principle during cholecystectomy. Re-operation time and surgical procedure are decided according to the type of IBDI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iatrogenic bile duct injuries--clinical problems.Pol Przegl Chir. 2014 Jan;86(1):17-25. doi: 10.2478/pjs-2014-0004. Pol Przegl Chir. 2014. PMID: 24578450
-
Bile duct injuries during open and laparoscopic cholecystectomy: management and outcome.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2013 May;11(24):187-93. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2013. PMID: 24362609
-
The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the management of iatrogenic bile duct injury after cholecystectomy.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2019 Sep;111(9):690-695. doi: 10.17235/reed.2019.6245/2019. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2019. PMID: 31368333
-
[Iatrogenic lesions of the biliary tract].Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2017 Oct-Dec;37(4):350-356. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2017. PMID: 29459806 Review. Spanish.
-
Bile duct injury after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The United States experience.Surg Endosc. 1998 Apr;12(4):315-21. doi: 10.1007/s004649900661. Surg Endosc. 1998. PMID: 9543520 Review.
Cited by
-
2020 WSES guidelines for the detection and management of bile duct injury during cholecystectomy.World J Emerg Surg. 2021 Jun 10;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13017-021-00369-w. World J Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 34112197 Free PMC article.
-
Biliary Cripple and the Spectrum of Complications following Cholecystectomy: A Case Report.Case Rep Surg. 2022 Sep 22;2022:5370722. doi: 10.1155/2022/5370722. eCollection 2022. Case Rep Surg. 2022. PMID: 36245685 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency percutaneous treatment in surgical bile duct injury.Emerg Radiol. 2008 Sep;15(5):335-41. doi: 10.1007/s10140-008-0719-0. Epub 2008 May 8. Emerg Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18463906
-
Long-Term Impact of Iatrogenic Bile Duct Injury.Dig Surg. 2020;37(1):10-21. doi: 10.1159/000496432. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Dig Surg. 2020. PMID: 30654363 Free PMC article.
-
Early or Delayed Intervention for Bile Duct Injuries following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy? A Dilemma Looking for an Answer.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:104235. doi: 10.1155/2015/104235. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 25722718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson BN, Parks RW, Madhavan KK, Wigmore SJ, Garden OJ. Early specialist repair of biliary injury. Br J Surg. 2006;93:216–220. - PubMed
-
- Diamantis T, Tsigris C, Kiriakopoulos A, Papalambros E, Bramis J, Michail P, Felekouras E, Griniatsos J, Rosenberg T, Kalahanis N, et al. Bile duct injuries associated with laparoscopic and open cholecystectomy: an 11-year experience in one institute. Surg Today. 2005;35:841–845. - PubMed
-
- Flum DR, Dellinger EP, Cheadle A, Chan L, Koepsell T. Intraoperative cholangiography and risk of common bile duct injury during cholecystectomy. JAMA. 2003;289:1639–1644. - PubMed
-
- Richardson MC, Bell G, Fullarton GM. Incidence and nature of bile duct injuries following laparoscopic cholecystectomy: an audit of 5913 cases. West of Scotland Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Audit Group. Br J Surg. 1996;83:1356–1360. - PubMed
-
- Mercado MA, Chan C, Orozco H, Tielve M, Hinojosa CA. Acute bile duct injury. The need for a high repair. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:1351–1355. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources