Change in nutritional status modulates the abundance of critical pre-initiation intermediate complexes during translation initiation in vivo
- PMID: 17512538
- PMCID: PMC2041914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.034
Change in nutritional status modulates the abundance of critical pre-initiation intermediate complexes during translation initiation in vivo
Abstract
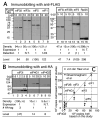
In eukaryotic translation initiation, eIF2GTP-Met-tRNA(i)(Met) ternary complex (TC) interacts with eIF3-eIF1-eIF5 complex to form the multifactor complex (MFC), while eIF2GDP associates with eIF2B for guanine nucleotide exchange. Gcn2p phosphorylates eIF2 to inhibit eIF2B. Here we evaluate the abundance of eIFs and their pre-initiation intermediate complexes in gcn2 deletion mutant grown under different conditions. We show that ribosomes are three times as abundant as eIF1, eIF2 and eIF5, while eIF3 is half as abundant as the latter three and hence, the limiting component in MFC formation. By quantitative immunoprecipitation, we estimate that approximately 15% of the cellular eIF2 is found in TC during rapid growth in a complex rich medium. Most of the TC is found in MFC, and important, approximately 40% of the total eIF2 is associated with eIF5 but lacks tRNA(i)(Met). When the gcn2Delta mutant grows less rapidly in a defined complete medium, TC abundance increases threefold without altering the abundance of each individual factor. Interestingly, the TC increase is suppressed by eIF5 overexpression and Gcn2p expression. Thus, eIF2B-catalyzed TC formation appears to be fine-tuned by eIF2 phosphorylation and the novel eIF2/eIF5 complex lacking tRNA(i)(Met).
Figures






References
-
- Pestova TV, Lorsch JR, Hellen CUT. The mechanism of translation initiation in eukaryotes. In: Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007. pp. 87–128.
-
- Hinnebusch AG, Dever TE, Asano K. Mechanism of translation initiation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In: Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007. pp. 225–268.
-
- Algire MA, Maag D, Lorsch JR. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol Cell. 2005;20:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

