Preparations and limitations for prevention of severe acute respiratory syndrome in a tertiary care centre of India
- PMID: 17512634
- PMCID: PMC7114601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2007.02.015
Preparations and limitations for prevention of severe acute respiratory syndrome in a tertiary care centre of India
Abstract
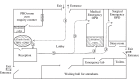
This short-term observational study of infection control practice was performed in the medical emergency outpatient department (EMOPD) of a tertiary-care hospital in India when threatened by an outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). An investigator attended the lobby daily to screen patients with symptoms for SARS. Patient/attendant load, patient flow, medical staff working practices and position in the EMOPD were observed. Infection control measures such as fumigation and cleaning were noted, as was the EMOPD laboratory function, use of personnel protection and display of information on infectious diseases. A total of 162 (7.4%) of the 2165 patients surveyed had respiratory symptoms but no cases of SARS were found. The flow of patients and their attendants was not systematic. No laboratory tests for SARS were available, and no educational material on SARS was displayed. The EMOPDs in key hospitals need be able to screen for infectious diseases, especially in view of the threats from SARS and Avian influenza.
Figures
References
-
- Singhi S., Jain V., Gupta G. Pediatric emergencies at a tertiary care hospital in India. J Trop Pediatr. 2003;49:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome – worldwide, 2003. MMWR Morb Mort Wkly Rep. 2003;52:226–228. - PubMed
-
- Directorate General of Health Services . New Delhi, DGHS, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India; 2006. Contingency plan for management of human cases of avian influenza.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous