Nanometer-sized diamond particle as a probe for biolabeling
- PMID: 17513352
- PMCID: PMC1959542
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.108134
Nanometer-sized diamond particle as a probe for biolabeling
Abstract
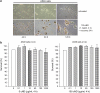
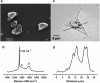
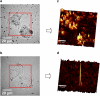
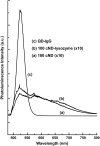
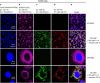
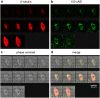
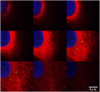
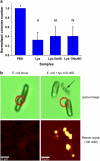
A novel method is proposed using nanometer-sized diamond particles as detection probes for biolabeling. The advantages of nanodiamond's unique properties were demonstrated in its biocompatibility, nontoxicity, easily detected Raman signal, and intrinsic fluorescence from its natural defects without complicated pretreatments. Carboxylated nanodiamond's (cND's) penetration ability, noncytotoxicity, and visualization of cND-cell interactions are demonstrated on A549 human lung epithelial cells. Protein-targeted cell interaction visualization was demonstrated with cND-lysozyme complex interaction with bacteria Escherichia coli. It is shown that the developed biomolecule-cND complex preserves the original functions of the test protein. The easily detected natural fluorescent and Raman intrinsic signals, penetration ability, and low cytotoxicity of cNDs render them promising agents in multiple medical applications.
Figures
References
-
- Poh, W. C., K. P. Loh, W. D. Zhang, S. Triparthy, J. S. Ye, and F. S. Sheu. 2004. Biosensing properties of diamond and carbon nanotubes. Langmuir. 20:5484–5492. - PubMed
-
- Carlise, J. A. 2004. Diamond films: Precious biosensors. Nat. Mater. 3:668–669. - PubMed
-
- Wang, J. 2005. Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis. 17:7–14.
-
- Sotiropoulou, S., V. Gavalas, V. Vamvakaki, and N. A. Chaniotakis. 2003. Novel carbon materials in biosensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 18:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Ushizawa, K., Y. Sato, T. Mitsumory, T. Machinami, T. Ueda, and T. Ando. 2002. Covalent immobilization of DNA on diamond and its verification by diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 351:105–108.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

