Effects of macromolecular crowding on biochemical reaction equilibria: a molecular thermodynamic perspective
- PMID: 17513384
- PMCID: PMC1948034
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.104646
Effects of macromolecular crowding on biochemical reaction equilibria: a molecular thermodynamic perspective
Abstract
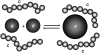
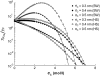
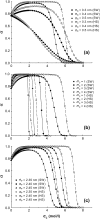
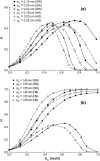
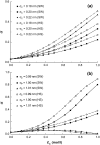
A molecular thermodynamic model is developed to investigate the effects of macromolecular crowding on biochemical reactions. Three types of reactions, representing protein folding/conformational isomerization, coagulation/coalescence, and polymerization/association, are considered. The reactants, products, and crowders are modeled as coarse-grained spherical particles or as polymer chains, interacting through hard-sphere interactions with or without nonbonded square-well interactions, and the effects of crowder size and chain length as well as product size are examined. The results predicted by this model are consistent with experimentally observed crowding effects based on preferential binding or preferential exclusion of the crowders. Although simple hard-core excluded-volume arguments do in general predict the qualitative aspects of the crowding effects, the results show that other intermolecular interactions can substantially alter the extent of enhancement or reduction of the equilibrium and can even change the direction of the shift. An advantage of the approach presented here is that competing reactions can be incorporated within the model.
Figures
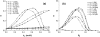
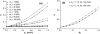
References
-
- Minton, A. P. 2001. The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media. J. Biol. Chem. 276:10577–10580. - PubMed
-
- Ellis, R. J., and A. P. Minton. 2003. Cell biology—Join the crowd. Nature. 425:27–28. - PubMed
-
- Sasahara, K., P. McPhie, and A. P. Minton. 2003. Effect of dextran on protein stability and conformation attributed to macromolecular crowding. J. Mol. Biol. 326:1227–1237. - PubMed
-
- Minton, A. P. 2005. Influence of macromolecular crowding upon the stability and state of association of proteins: predictions and observations. J. Pharm. Sci. 94:1668–1675. - PubMed
-
- Hall, D., and A. P. Minton. 2003. Macromolecular crowding: qualitative and semiquantitative successes, quantitative challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Proteins Proteom. 1649:127–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

