Correlation between asparaginase sensitivity and asparagine synthetase protein content, but not mRNA, in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines
- PMID: 17514734
- PMCID: PMC8441542
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.21213
Correlation between asparaginase sensitivity and asparagine synthetase protein content, but not mRNA, in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines
Abstract
Background: Asparaginase (ASNase) is an essential component of most treatment protocols for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Although increased asparagine synthetase (ASNS) expression may contribute to ASNase resistance, there is conflicting data from patient samples with regard to correlation between ASNS mRNA content and ASNase sensitivity.
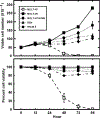
Procedure: Both T-cell and B-cell derived ALL cell lines were treated with ASNase and then monitored for cell proliferation, cell death, and ASNS mRNA and protein expression.
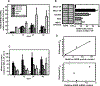
Results: Despite elevated ASNS mRNA following ASNase treatment, different ALL cell lines varied widely in translation to ASNS protein. Although ASNS mRNA levels did not consistently reflect ASNase sensitivity, there was an inverse correlation between ASNS protein and ASNase-induced cell death. Expression of ASNS in an ASNase-sensitive cell line resulted in enhanced ASNase resistance, and conversely, siRNA-mediated inhibition of ASNS expression promoted increased drug sensitivity.
Conclusions: These observations provide an explanation for the ASNase sensitivity of ALL cells and demonstrate the importance of measuring ASNS protein rather than mRNA in predicting ASNase responsiveness.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Sallan SE, Hitchcock-Bryan S, Gelber R, et al.Influence of intensive asparaginase in the treatment of childhood non-T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 1983;43:5601–5607. - PubMed
-
- Amylon MD, Shuster J, Pullen J, et al.Intensive high-dose asparaginase consolidation improves survival for pediatric patients with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and advanced stage lymphoblastic lymphoma: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. Leukemia 1999;13:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Cooney DA, Capizzi RL, Handshumacher RE. Evaluation of L-asparagine metabolism in animals and man. Cancer Res1970;30: 929–935. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Pan YX, Dudenhausen EE, et al.Amino acid deprivation induces the transcription rate of the human asparagine synthetase gene through a timed program of expression and promoter binding of nutrient-responsive bZIP transcription factors as well as localized histone acetylation. J Biol Chem 2004;279:50829–50839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

