Genomic analyses of transcription factor binding, histone acetylation, and gene expression reveal mechanistically distinct classes of estrogen-regulated promoters
- PMID: 17515612
- PMCID: PMC1951957
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00083-07
Genomic analyses of transcription factor binding, histone acetylation, and gene expression reveal mechanistically distinct classes of estrogen-regulated promoters
Abstract
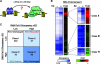
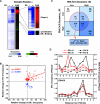
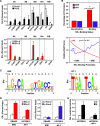
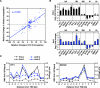
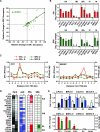
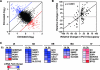
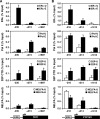
To explore the global mechanisms of estrogen-regulated transcription, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with DNA microarrays to determine the localization of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha), steroid receptor coactivator proteins (SRC), and acetylated histones H3/H4 (AcH) at estrogen-regulated promoters in MCF-7 cells with or without estradiol (E2) treatment. In addition, we correlated factor occupancy with gene expression and the presence of transcription factor binding elements. Using this integrative approach, we defined a set of 58 direct E2 target genes based on E2-regulated Pol II occupancy and classified their promoters based on factor binding, histone modification, and transcriptional output. Many of these direct E2 target genes exhibit interesting modes of regulation and biological activities, some of which may be relevant to the onset and proliferation of breast cancers. Our studies indicate that about one-third of these direct E2 target genes contain promoter-proximal ERalpha-binding sites, which is considerably more than previous estimates. Some of these genes represent possible novel targets for regulation through the ERalpha/AP-1 tethering pathway. Our studies have also revealed several previously uncharacterized global features of E2-regulated gene expression, including strong positive correlations between Pol II occupancy and AcH levels, as well as between the E2-dependent recruitment of ERalpha and SRC at the promoters of E2-stimulated genes. Furthermore, our studies have revealed new mechanistic insights into E2-regulated gene expression, including the absence of SRC binding at E2-repressed genes and the presence of constitutively bound, promoter-proximally paused Pol IIs at some E2-regulated promoters. These mechanistic insights are likely to be relevant for understanding gene regulation by a wide variety of nuclear receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Acevedo, M. L., K. C. Lee, J. D. Stender, B. S. Katzenellenbogen, and W. L. Kraus. 2004. Selective recognition of distinct classes of coactivators by a ligand-inducible activation domain. Mol. Cell 13:725-738. - PubMed
-
- Aiyar, S. E., J. L. Sun, A. L. Blair, C. A. Moskaluk, Y. Z. Lu, Q. N. Ye, Y. Yamaguchi, A. Mukherjee, D. M. Ren, H. Handa, and R. Li. 2004. Attenuation of estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcription through estrogen-stimulated recruitment of a negative elongation factor. Genes Dev. 18:2134-2146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrau, J. C., L. van de Pasch, P. Lijnzaad, T. Bijma, M. G. Koerkamp, J. van de Peppel, M. Werner, and F. C. Holstege. 2006. Genome-wide location of the coactivator mediator: binding without activation and transient Cdk8 interaction on DNA. Mol. Cell 22:179-192. - PubMed
-
- Blais, A., and B. D. Dynlacht. 2005. Constructing transcriptional regulatory networks. Genes Dev. 19:1499-1511. - PubMed
-
- Bodescot, M., and O. Brison. 1996. Characterization of new human c-myc mRNA species produced by alternative splicing. Gene 174:115-120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
