An interferon signature in the peripheral blood of dermatomyositis patients is associated with disease activity
- PMID: 17515957
- PMCID: PMC1869622
- DOI: 10.2119/2006-00085.Baechler
An interferon signature in the peripheral blood of dermatomyositis patients is associated with disease activity
Abstract
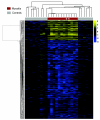
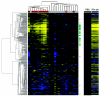
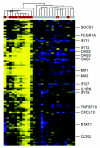
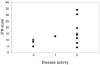
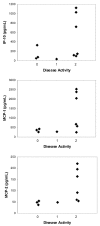
Recent studies have shown increased expression of interferon (IFN)-regulated genes in the peripheral blood cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A similar interferon signature has been observed in affected muscle tissue from patients with dermatomyositis (DM), but it has not yet been determined if this signature extends to the peripheral blood in DM. We performed global gene expression profiling of peripheral blood cells from adult and juvenile DM patients and healthy controls. Several interesting groups of genes were differentially expressed in DM, including genes with immune function, and others that function in muscle or are involved in mitochondrial/oxidative phosphorylation. Investigation of type I IFN-regulated transcripts revealed a striking interferon signature present in most DM patients studied. Levels of type I IFN-regulated proteins were also elevated in DM serum samples. Furthermore, both the transcript and serum protein IFN signatures were associated with disease activity. These data suggest that the IFN signature may be a useful marker for DM disease activity, and that sampling peripheral blood may be a more practical alternative to muscle biopsy for measuring this signature.
Figures

References
-
- Mastaglia FL, Phillips BA. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: epidemiology, classification, and diagnostic criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2002;28:723–41. - PubMed
-
- Reed AM. Myositis in children. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:428–33. - PubMed
-
- O’Hanlon TP, et al. Immunogenetic risk and protective factors for the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: distinct HLA-A, -B, -Cw, -DRB1 and -DQA1 allelic profiles and motifs define clinicopathologic groups in caucasians. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005;84:338–49. - PubMed
-
- Christensen ML, Pachman LM, Schneiderman R, Patel DC, Friedman JM. Prevalence of Cox-sackie B virus antibodies in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29:1365–70. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg SA, et al. Interferon-alpha/beta-mediated innate immune mechanisms in dermatomyositis. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:664–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
