Double-stranded DNA and double-stranded RNA induce a common antiviral signaling pathway in human cells
- PMID: 17517627
- PMCID: PMC1885623
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0703285104
Double-stranded DNA and double-stranded RNA induce a common antiviral signaling pathway in human cells
Abstract
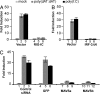
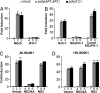
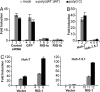
Virus infection triggers IFN immune defenses in infected cells in part through viral nucleic acid interactions, but the pathways by which dsDNA and DNA viruses trigger innate defenses are only partially understood. Here we present evidence that both retinoic acid-induced gene I (RIG-I) and mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) are required for dsDNA-induced IFN-beta promoter activation in a human hepatoma cell line (Huh-7), and that activation is efficiently blocked by the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease, which is known to block dsRNA signaling by cleaving MAVS. These findings suggest that dsDNA and dsRNA share a common pathway to trigger the innate antiviral defense response in human cells, although dsDNA appears to trigger that pathway upstream of the dsRNA-interacting protein RIG-I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Akira S, Fujita T. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:730–737. - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Matsumoto K, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Foy E, Loo YM, Gale M, Jr, Akira S, et al. J Immunol. 2005;175:2851–2858. - PubMed
-
- Hiscott J, Lin R, Nakhaei P, Paz S. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12:53–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

