Effects of rifampin and multidrug resistance gene polymorphism on concentrations of moxifloxacin
- PMID: 17517835
- PMCID: PMC1932492
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01621-06
Effects of rifampin and multidrug resistance gene polymorphism on concentrations of moxifloxacin
Abstract
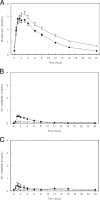
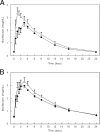
Treatment regimens combining moxifloxacin and rifampin for drug-susceptible tuberculosis are being studied intensively. However, rifampin induces enzymes that transport and metabolize moxifloxacin. We evaluated the effect of rifampin and the human multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) C3435T polymorphisms (P-glycoprotein) on moxifloxacin pharmacokinetic parameters. This was a single-center, sequential design study with 16 volunteers in which sampling was performed after four daily oral doses of moxifloxacin (400 mg) and again after 10 days of combined rifampin (600 mg) and moxifloxacin. After daily coadministration of rifampin, the area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h (AUC(0-24)) for moxifloxacin decreased 27%. Average bioequivalence between moxifloxacin coadministered with rifampin and moxifloxacin alone was not demonstrated: the ratio of geometric means (RGM) of the moxifloxacin AUC(0-24) was 73.3 (90% confidence intervals [CI], 64.3, 83.5) (total P value, 0.87 for two one-sided t tests). Peak moxifloxacin concentrations, however, were equivalent: the RGM of the maximum concentration of the drug in serum was 93.6 (90% CI, 80.2, 109.3) (total P value, 0.049). Concentrations of the sulfate conjugate metabolite of moxifloxacin were increased twofold following rifampin coadministration (AUC(0-24), 1.29 versus 2.79 mug.h/ml). Concomitant rifampin administration resulted in a 27% decrease in the mean moxifloxacin AUC(0-24) and a marked increase in the AUC(0-24) of the microbiologically inactive M1 metabolite. Additional studies are required to understand the clinical significance of the moxifloxacin-rifampin interaction.
Figures
References
-
- Burman, W. J., S. Goldberg, J. L. Johnson, G. Muzanye, M. Engle, A. W. Mosher, S. Choudhri, C. L. Daley, S. S. Munsiff, Z. Zhao, A. Vernon, R. E. Chaisson, and the Tuberculosis Trials Consortium. 2006. Moxifloxacin versus ethambutol in the first 2 months of treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 174:331-338. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program, National Cancer Institute. 30 April 1999, posting date. Common toxicity criteria, version 2.0. http://ctep.cancer.gov/forms/CTCv20_4-30-992.pdf.
-
- de Lange, E., S. Marchand, D. van den Berg, I. van der Sandt, A. de Boer, A. Delon, S. Bouquet, and W. Couet. 2000. In vitro and in vivo investigations on fluoroquinolones; effects of the P-glycoprotein efflux transporter on brain distribution of sparfloxacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 12:85-93. - PubMed
-
- Dilger, K., B. Greiner, M. F. Fromm, U. Hofmann, H. K. Kroemer, and M. Eichelbaum. 1999. Consequences of rifampin treatment on propafenone disposition in extensive and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 9:551-559. - PubMed
-
- Eichelbaum, M., M. Fromm, and M. Shwab. 2004. Clinical aspects of the MDR1 (ABCB1) gene polymorphism. Ther. Drug Monit. 26:180-185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

