Early bactericidal activity of high-dose rifampin in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis evidenced by positive sputum smears
- PMID: 17517849
- PMCID: PMC1932511
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01474-06
Early bactericidal activity of high-dose rifampin in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis evidenced by positive sputum smears
Abstract
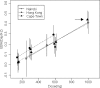
We studied the early bactericidal activity of twice the standard dose of rifampin in subjects with pulmonary tuberculosis evidenced by positive smears. The observed mean 2-day activity was almost double that reported at the standard dose. Further studies are warranted to establish whether higher rifampin doses might assist in shortening tuberculosis treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Acocella, G. 1983. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of rifampin in humans. Rev. Infect. Dis. 5(Suppl. 3):S428-S432. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand, A. 1994. Antibiotic treatment of brucellosis. Presse Med. 23:1128-1131. - PubMed
-
- Chan, S. L., W. W. Yew, W. K. Ma, D. J. Girling, V. R. Aber, D. Felmingham, B. W. Allen, and D. A. Mitchison. 1992. The early bactericidal activity of rifabutin measured by sputum viable counts in Hong Kong patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuber. Lung Dis. 73:33-38. - PubMed
-
- Grosset, J., and S. Leventis. 1983. Adverse effects of rifampin. Rev. Infect. Dis. 5(Suppl. 3):S440-S450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

