Caveolin-1 regulates cell polarization and directional migration through Src kinase and Rho GTPases
- PMID: 17517963
- PMCID: PMC2064213
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200701006
Caveolin-1 regulates cell polarization and directional migration through Src kinase and Rho GTPases
Abstract
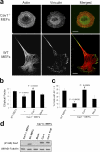
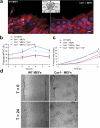
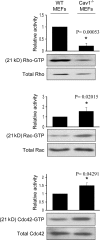
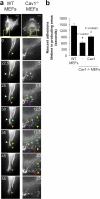
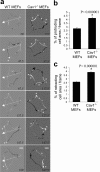
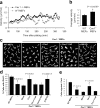
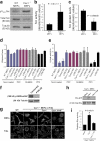
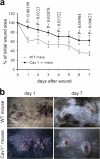
Development, angiogenesis, wound healing, and metastasis all involve the movement of cells in response to changes in the extracellular environment. To determine whether caveolin-1 plays a role in cell migration, we have used fibroblasts from knockout mice. Caveolin-1-deficient cells lose normal cell polarity, exhibit impaired wound healing, and have decreased Rho and increased Rac and Cdc42 GTPase activities. Directional persistency of migration is lost, and the cells show an impaired response to external directional stimuli. Both Src inactivation and p190RhoGAP knockdown restore the wild-type phenotype to caveolin-1-deficient cells, suggesting that caveolin-1 stimulates normal Rho GTP loading through inactivation of the Src-p190RhoGAP pathway. These findings highlight the importance of caveolin-1 in the establishment of cell polarity during directional migration through coordination of the signaling of Src kinase and Rho GTPases.
Figures
References
-
- Arthur, W.T., L.A. Petch, and K. Burridge. 2000. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 10:719–722. - PubMed
-
- Beardsley, A., K. Fang, H. Mertz, V. Castranova, S. Friend, and J. Liu. 2005. Loss of caveolin-1 polarity impedes endothelial cell polarization and directional movement. J. Biol. Chem. 280:3541–3547. - PubMed
-
- Brouns, M.R., S.F. Matheson, and J. Settleman. 2001. p190 RhoGAP is the principal Src substrate in brain and regulates axon outgrowth, guidance and fasciculation. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:361–367. - PubMed
-
- Burridge, K., and K. Wennerberg. 2004. Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell. 116:167–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

