Characterisation and radioimmunotherapy of L19-SIP, an anti-angiogenic antibody against the extra domain B of fibronectin, in colorectal tumour models
- PMID: 17519905
- PMCID: PMC2359968
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603806
Characterisation and radioimmunotherapy of L19-SIP, an anti-angiogenic antibody against the extra domain B of fibronectin, in colorectal tumour models
Abstract
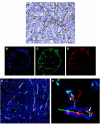
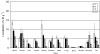
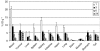
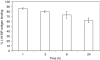
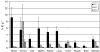
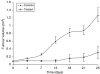
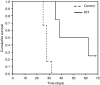
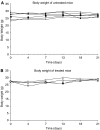
Angiogenesis is a characteristic feature of tumours and other disorders. The human monoclonal antibody L19- SIP targets the extra domain B of fibronectin, a marker of angiogenesis expressed in a range of tumours. The aim of this study was to investigate whole body distribution, tumour localisation and the potential of radioimmunotherapy with the L19-small immunoprotein (SIP) in colorectal tumours. Two colorectal tumour models with highly different morphologies, the SW1222 and LS174T xenografts, were used in this study. Localisation and retention of the L19-SIP antibody at tumour vessels was demonstrated using immunohistochemistry and Cy3-labelled L19-SIP. Whole body biodistribution studies in both tumour models were carried out with (125)I-labelled L19-SIP. Finally, (131)I-labelled antibody was used to investigate the potential of radioimmunotherapy in SW1222 tumours. Using immunohistochemistry, we confirmed extra domain B expression in the tumour vasculature. Immunofluorescence demonstrated localisation and retention of injected Cy3-labelled L19-SIP at the abluminal side of tumour vessels. Biodistribution studies using a (125)I-labelled antibody showed selective tumour uptake in both models. Higher recorded values for localisation were found in the SW1222 tumours than in the LS174T (7.9 vs 6.6 %ID g(-1)), with comparable blood clearance for both models. Based on these results, a radioimmunotherapy study was performed in the SW1222 xenograft using (131)I-Labelled L19-SIP (55.5 MBq), which showed selective tumour uptake, tumour growth inhibition and improved survival. Radio- and fluorescence-labelled L19-SIP showed selective localisation and retention at vessels of two colorectal xenografts. Furthermore, (131)I-L19-SIP shows potential as a novel treatment of colorectal tumours, and provides the foundation to investigate combined therapies in the same tumour models.
Figures
References
-
- Alessi P, Ebbinghaus C, Neri D (2004) Molecular targeting of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1654(1): 39–49 - PubMed
-
- Berndorff D, Borkowski S, Sieger S, Rother A, Friebe M, Viti F, Hilger CS, Cyr JE, Dinkelborg LM (2005) Radioimmunotherapy of solid tumours by targeting extra domain B fibronectin: identification of the best-suited radioimmunoconjugate. Clin Cancer Res 11(19 Part 2): 7053s–7063s - PubMed
-
- Birchler M, Viti F, Zardi L, Spiess B, Neri D (1999) Selective targeting and photocoagulation of ocular angiogenesis mediated by a phage-derived human antibody fragment. Nat Biotechnol 17(10): 984–988 - PubMed
-
- Birchler MT, Milisavlijevic D, Pfaltz M, Neri D, Odermatt B, Schmid S, Stoeckli SJ (2003) Expression of the extra domain B of fibronectin, a marker of angiogenesis, in head and neck tumours. Laryngoscope 113(7): 123 - PubMed
-
- Borsi L, Balza E, Bestagno M, Castellani P, Carnemolla B, Biro A, Leprini A, Sepulveda J, Burrone O, Neri D, Zardi L (2002) Selective targeting of tumoural vasculature: comparison of different formats of an antibody (L19) to the ED-B domain of fibronectin. Int J Cancer 102(1): 75–85 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

