Direct repair of defects in lumbar spondylolysis with a new pedicle screw hook fixation: clinical, functional and Ct-assessed study
- PMID: 17520298
- PMCID: PMC2078304
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-007-0392-0
Direct repair of defects in lumbar spondylolysis with a new pedicle screw hook fixation: clinical, functional and Ct-assessed study
Abstract
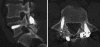
Spondylolysis is a common entity, a minority of people affected by this disease need medical care, and only a few require surgery. Reconstruction of the pars interarticularis is an interesting alternative to segmental fusion; this technique has the advantage of preserving segmental motion. Most authors report good results for young patients without intervertebral disk or facet degenerative changes. Moreover Louis also showed good to excellent results with his technique carried out among people who presented a satisfactory disk height (equal to two thirds of normal height). This could extend the number of patients for whom pars interarticularis repair could be proposed. In this study, the limit of reconstruction was set at grade 3 of the Pfirrmann's classification. The fixation of the isthmus was done with a new kind of pedicle screw hook system. This stable and strong device is easy to use, allows an anatomic pars interarticularis reconstruction of spondylolysis and avoids a postoperative bracing. Twenty-three patients were assessed in this study, the mean age at operation was 34 (range 16-52 years) and the average follow-up was for 59 months (range 6-113 months). Eight patients showed moderate degenerative disk disease before the surgery and 12 patients had a grade 1 spondylolisthesis. The visual analogical scale, the Oswestry disability index (ODI) and the modified Prolo score were used for assessment of pain and clinical outcome before and after surgery. The results were from "excellent" to "good" for twenty patients (87%) and "fair" for three of them (13%). The consolidation of the isthmus was assessed at the end of the study (CT-scan); the fusion rate was observed in 91%. Among patients aged less than 30 years results are from "good", to "excellent" in all cases and consolidation was always observed. All of them showed normal disc signal before the surgery. In the group aged more than 30 years, the results varied from "good" to "excellent' in 73% and fusion of the defect was discovered in 82% of cases. Eight of them (73%) had moderate disk signal modification before the surgery. All people with fair results displayed moderate disk degeneration signs at MRI before surgery; but two of those three patients had a failure of defect consolidation too and it is also associated with poor results by several authors. No complication was found in this series. According to the good results reported by Louis and upto the current finding, the authors believe that pars interarticularis repair can be carried out on patients with moderate degenerative disk disease; the stage 3 of Pfirrmann's classification seems a good limit. The Bone and joint research (B.J.R. system) is readily usable by any surgeon using pedicle screw systems and having a short learning curve. No device failure has been observed in this series.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous