High synovial expression of the inhibitory FcgammaRIIb in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17521421
- PMCID: PMC2206344
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2206
High synovial expression of the inhibitory FcgammaRIIb in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
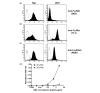
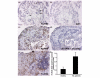
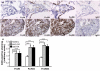
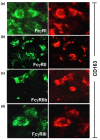
Activating Fc gamma receptors (FcgammaRs) have been identified as having important roles in the inflammatory joint reaction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and murine models of arthritis. However, the role of the inhibitory FcgammaRIIb in the regulation of the synovial inflammation in RA is less known. Here we have investigated synovial tissue from RA patients using a novel monoclonal antibody (GB3) specific for the FcgammaRIIb isoform. FcgammaRIIb was abundantly expressed in synovia of RA patients, in sharp contrast to the absence or weak staining of FcgammaRIIb in synovial biopsies from healthy volunteers. In addition, the expression of FcgammaRI, FcgammaRII and FcgammaRIII was analyzed in synovia obtained from early and late stages of RA. Compared with healthy synovia, which expressed FcgammaRII, FcgammaRIII but not FcgammaRI, all activating FcgammaRs were expressed and significantly up-regulated in RA, regardless of disease duration. Macrophages were one of the major cell types in the RA synovium expressing FcgammaRIIb and the activating FcgammaRs. Anti-inflammatory treatment with glucocorticoids reduced FcgammaR expression in arthritic joints, particularly that of FcgammaRI. This study demonstrates for the first time that RA patients do not fail to up-regulate FcgammaRIIb upon synovial inflammation, but suggests that the balance between expression of the inhibitory FcgammaRIIb and activating FcgammaRs may be in favour of the latter throughout the disease course. Anti-inflammatory drugs that target activating FcgammaRs may represent valuable therapeutics in this disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Activating and inhibitory Fc gamma receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: from treatment to targeted therapies.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):106. doi: 10.1186/ar2224. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17764583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, Sundin U, van Venrooij WJ. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2741–2749. doi: 10.1002/art.11223. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

