A critical period for enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated neurons of the adult brain
- PMID: 17521569
- PMCID: PMC2040308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.05.002
A critical period for enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated neurons of the adult brain
Abstract
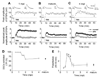
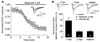
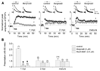
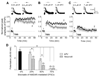
Active adult neurogenesis occurs in discrete brain regions of all mammals and is widely regarded as a neuronal replacement mechanism. Whether adult-born neurons make unique contributions to brain functions is largely unknown. Here we systematically characterized synaptic plasticity of retrovirally labeled adult-born dentate granule cells at different stages during their neuronal maturation. We identified a critical period between 1 and 1.5 months of the cell age when adult-born neurons exhibit enhanced long-term potentiation with increased potentiation amplitude and decreased induction threshold. Furthermore, such enhanced plasticity in adult-born neurons depends on developmentally regulated synaptic expression of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Our study demonstrates that adult-born neurons exhibit the same classic critical period plasticity as neurons in the developing nervous system. The transient nature of such enhanced plasticity may provide a fundamental mechanism allowing adult-born neurons within the critical period to serve as major mediators of experience-induced plasticity while maintaining stability of the mature circuitry.
Figures
References
-
- Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M. Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev. 2005;85:523–569. - PubMed
-
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Malinow R. NMDA Receptor Subunit Composition Controls Synaptic Plasticity by Regulating Binding to CaMKII. Neuron. 2005;48:289–301. - PubMed
-
- Barth AL, Malenka RC. NMDAR EPSC kinetics do not regulate the critical period for LTP at thalamocortical synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:235–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

